Page 65 - DMGT405_FINANCIAL%20MANAGEMENT
P. 65
Unit 4: Concept of Economic Value Added
Differences between ROI and EVA Notes
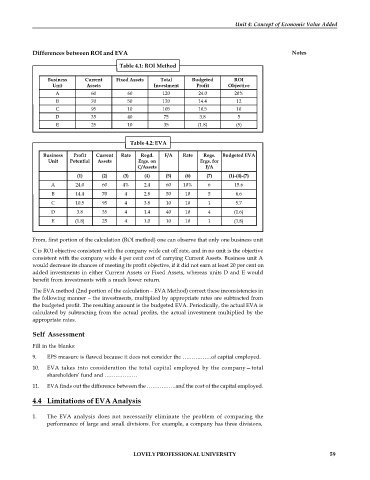
Table 4.1: ROI Method
Business Current Fixed Assets Total Budgeted ROI
Unit Assets Investment Profit Objective
A 60 60 120 24.0 20%
B 70 50 120 14.4 12
C 95 10 105 10.5 10
D 35 40 75 3.8 5
E 25 10 35 (1.8) (5)
Table 4.2: EVA
Business Profit Current Rate Regd. F/A Rate Regs. Budgeted EVA
Unit Potential Assets Ergs. on Ergs. for
C/Assets F/A
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (1)-(4)-(7)
A 24.0 60 4% 2.4 60 10% 6 15.6
B 14.4 70 4 2.8 50 10 5 6.6
C 10.5 95 4 3.8 10 10 1 5.7
D 3.8 35 4 1.4 40 10 4 (1.6)
E (1.8) 25 4 1.0 10 10 1 (3.8)
From, first portion of the calculation (ROI method) one can observe that only one business unit
C is ROI objective consistent with the company wide cut off rate, and in no unit is the objective
consistent with the company wide 4 per cent cost of carrying Current Assets. Business unit A
would decrease its chances of meeting its profit objective, if it did not earn at least 20 per cent on
added investments in either Current Assets or Fixed Assets, whereas units D and E would
benefit from investments with a much lower return.
The EVA method (2nd portion of the calculation – EVA Method) correct these inconsistencies in
the following manner – the investments, multiplied by appropriate rates are subtracted from
the budgeted profit. The resulting amount is the budgeted EVA. Periodically, the actual EVA is
calculated by subtracting from the actual profits, the actual investment multiplied by the
appropriate rates.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
9. EPS measure is flawed because it does not consider the …………….of capital employed.
10. EVA takes into consideration the total capital employed by the company—total
shareholders’ fund and ………………
11. EVA finds out the difference between the …………….and the cost of the capital employed.
4.4 Limitations of EVA Analysis
1. The EVA analysis does not necessarily eliminate the problem of comparing the
performance of large and small divisions. For example, a company has three divisions,
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 59