Page 70 - DECO303_INDIAN_ECONOMY_ENGLISH
P. 70
Unit 5: Unemployment in India
and communication are the only way to trade and commerce. Since there is lack of transport Notes
and communication in rural areas, therefore, it leads to unemployment problem among
the villagers.
9. Inadequate Employment Planning: The employment arrangement of the government is
not satisfactory in assessment to population growth. In India nearly two lakh people are
added yearly to our existing population. But the employment prospects did not increase
according to the proportionate rate of population growth. As a result, a great alteration is
noticeable between the job occasions and population growth.
On the other hand, it is a very problematic task on the part of the Government to deliver
acceptable job services to all the people. Moreover, the government also does not take
tolerable step in this direction. The faulty service planning of the Government advances
this problem to a great extent. As a result, the problem of unemployment is increasing
every day.
5.3 Unemployment Types and Causes
This section emphasises on the unemployment types and causes. There are numerous types of
joblessness, each one well-defined in terms of cause and severity:
1. Cyclical: Cyclical joblessness/unemployment occurs when individuals drop their jobs as
an effect of a downturn in aggregate demand (AD). If the failure in aggregate demand is
determined, and the joblessness long-term, it is called either demand deficient, overall, or
Keynesian unemployment. For example, unemployment levels of 3 million were touched
in the UK in the last two recessions. In the most recent recession of 2008-2010,
unemployment levels rose to 2.4m in the last quarter of 2009, and are likely to peak at over
2.5m during 2010.
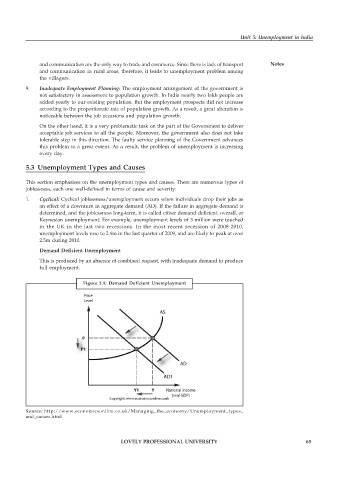
Demand Deficient Unemployment
This is produced by an absence of combined request, with inadequate demand to produce
full employment.
Figure 5.1: Demand Deficient Unemployment
Source: http://www.economicsonline.co.uk/Managing_the_economy/Unemployment_types_
and_causes.html
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 65