Page 238 - DCOM302_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 238
Unit 11: Marginal Costing and Profi t Planning
Notes
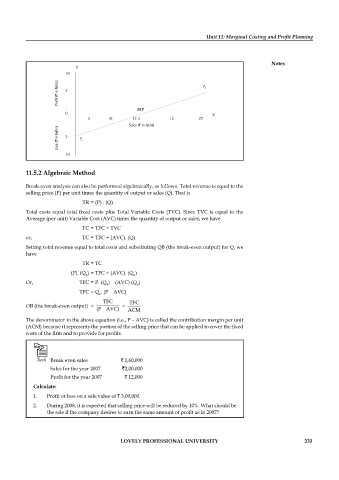
Y
10
Profit (Rs. in lakhs) Profi t (` in lakhs) 5 P 2
BEP
0 X
5 10 Sales (Rs. in lakhs) 15 20
12.5
Loss (Rs. in lakhs) Loss (` in lakhs) 5 P 1
Sales (` in lakhs)
10
11.5.2 Algebraic Method
Break-even analysis can also be performed algebraically, as follows. Total revenue is equal to the
selling price (P) per unit times the quantity of output or sales (Q). That is
TR = (P) . (Q)
Total costs equal total fixed costs plus Total Variable Costs (TVC). Since TVC is equal to the
Average (per unit) Variable Cost (AVC) times the quantity of output or sales, we have
TC = TFC + TVC
or, TC = TFC + (AVC). (Q)
Setting total revenue equal to total costs and substituting QB (the break-even output) for Q, we
have
TR = TC
(P). (Q ) = TFC + (AVC). (Q )
B B
Or, TFC = P. (Q ) – (AVC) (Q )
B B
TFC = Q . (P – AVC)
B
TFC TFC
OB (the break-even output) = =
(P – AVC) ACM
The denominator in the above equation (i.e., P – AVC) is called the contribution margin per unit
(ACM) because it represents the portion of the selling price that can be applied to cover the fi xed
costs of the firm and to provide for profi ts.
Task Break even sales ` 1,60,000
Sales for the year 2007 `2,00,000
Profit for the year 2007 ` 12,000
Calculate:
1. Profit or loss on a sale value of ` 3,00,000.
2. During 2008, it is expected that selling price will be reduced by 10%. What should be
the sale if the company desires to earn the same amount of profit as in 2007?
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 233