Page 236 - DCOM302_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 236
Unit 11: Marginal Costing and Profi t Planning
Of the two break-even points, only the first, corresponding to output rate Q is relevant. When a Notes
1
firm begins production, management usually expects to incur losses. But it is important to know
at what output rate the firm will go from a loss to a profit situation. In Figure 11.2 the fi rm would
want to get to the break-even output rate Q as soon as possible and then of course, move to the
1
profit maximising rate Q*. However, the firm would not expand production beyond Q* because
this would result in a reduction of profi t.
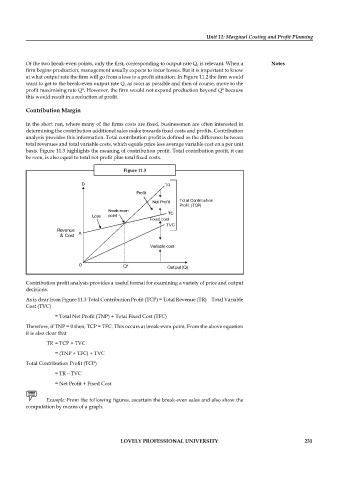
Contribution Margin
In the short run, where many of the firms costs are fixed, businessmen are often interested in
determining the contribution additional sales make towards fixed costs and profi ts. Contribution
analysis provides this information. Total contribution profit is defined as the difference between
total revenues and total variable costs, which equals price less average variable cost on a per unit
basis. Figure 11.3 highlights the meaning of contribution profi t. Total contribution profi t, it can
be seen, is also equal to total net profit plus total fi xed costs.
Figure 11.3
D TR
Profit
Net Profit Total Contribution
Profit (TCP)
Break-even
Loss point TC
Fixed cost
TVC
Revenue
A
& Cost
Variable cost
0 Q* Output(Q)
Contribution profit analysis provides a useful format for examining a variety of price and output
decisions.
As is clear from Figure 11.3 Total Contribution Profit (TCP) = Total Revenue (TR) – Total Variable
Cost (TVC)
= Total Net Profit (TNP) + Total Fixed Cost (TFC)
Therefore, if TNP = 0 then, TCP = TFC. This occurs at break-even point. From the above equation
it is also clear that
TR = TCP + TVC
= (TNP + TFC) + TVC
Total Contribution Profi t (TCP)
= TR – TVC
= Net Profit + Fixed Cost
Example: From the following figures, ascertain the break-even sales and also show the
computation by means of a graph.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 231