Page 195 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 195
Managerial Economics
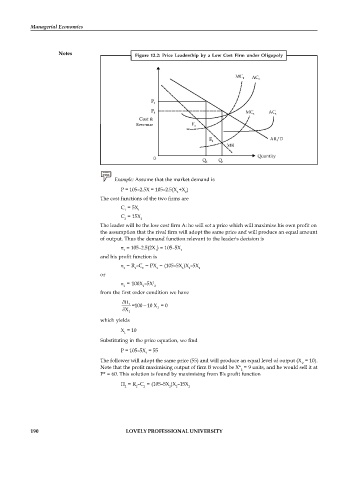
Notes Figure 12.2: Price Leadership by a Low Cost Firm under Oligopoly
Example: Assume that the market demand is
P = 105–2.5X = 105–2.5(X +X )
1 2
The cost functions of the two firms are
C = 5X
1 1
C = 15X
2 2
The leader will be the low cost firm A: he will set a price which will maximise his own profit on
the assumption that the rival firm will adopt the same price and will produce an equal amount
of output. Thus the demand function relevant to the leader's decision is
= 105–2.5(2X ) = 105–5X
1 1 1
and his profit function is
= R –C = PX = (105–5X )X –5X
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
or
= 100X –5X 1
1 1 2
from the first order condition we have
¶P 1 =100 10 X = 0
-
¶ X 1 1
which yields
X = 10
1
Substituting in the price equation, we find
P = 105–5X = 55
1
The follower will adopt the same price (55) and will produce an equal level of output (X = 10).
2
Note that the profit maximising output of firm B would be X* = 9 units, and he would sell it at
2
P* = 60. This solution is found by maximising from B's profit function
P = R –C = (105–5X )X –15X
2 2 2 2 2 2
190 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY