Page 196 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 196
Unit 12: Oligopoly
Notes
Task Two duopolist manufacture identical radio sets. The total cost of an output
é 1 2 ù
x sets per month in ` ê x + 3x 100 for each duopolist. When the price is ` p per set, the
+
ú
ë 25 û
market demand is x = 75 – 3p per month. What is the total equilibrium output per month.
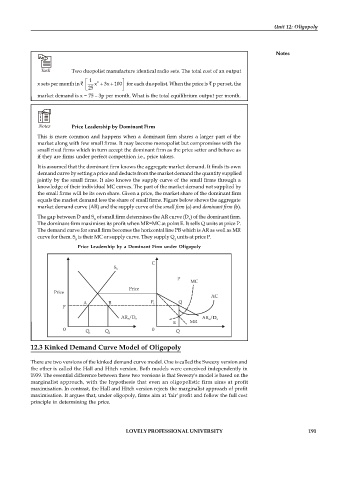
Notes Price Leadership by Dominant Firm
This is more common and happens when a dominant firm shares a larger part of the
market along with few small firms. It may become monopolist but compromises with the
small rival firms which in turn accept the dominant firm as the price setter and behave as
if they are firms under perfect competition i.e., price takers.
It is assumed that the dominant firm knows the aggregate market demand. It finds its own
demand curve by setting a price and deducts from the market demand the quantity supplied
jointly by the small firms. It also knows the supply curve of the small firms through a
knowledge of their individual MC curves. The part of the market demand not supplied by
the small firms will be its own share. Given a price, the market share of the dominant firm
equals the market demand less the share of small firms. Figure below shows the aggregate
market demand curve (AR) and the supply curve of the small firm (a) and dominant firm (b).
The gap between D and S of small firm determines the AR curve (D ) of the dominant firm.
S L
The dominant firm maximises its profit when MR=MC at point E. It sells Q units at price P.
The demand curve for small firm becomes the horizontal line PB which is AR as well as MR
curve for them. S is their MC or supply curve. They supply Q units at price P.
S 1
Price Leadership by a Dominant Firm under Oligopoly
12.3 Kinked Demand Curve Model of Oligopoly
There are two versions of the kinked demand curve model. One is called the Sweezy version and
the other is called the Hall and Hitch version. Both models were conceived independently in
1939. The essential difference between these two versions is that Sweezy's model is based on the
marginalist approach, with the hypothesis that even an oligopolistic firm aims at profit
maximisation. In contrast, the Hall and Hitch version rejects the marginalist approach of profit
maximisation. It argues that, under oligopoly, firms aim at 'fair' profit and follow the full cost
principle in determining the price.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 191