Page 202 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 202
Research Methodology
Notes A Linear Model
A linear model for the above data is
ˆ y = – 37 + 5.1x
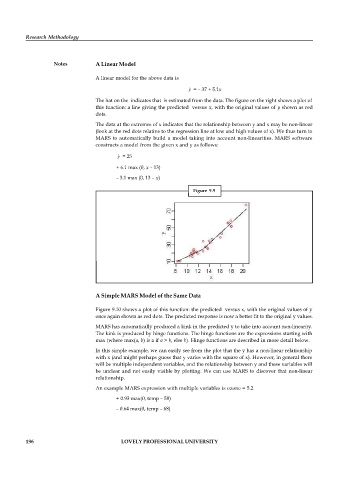
The hat on the indicates that is estimated from the data. The figure on the right shows a plot of
this function: a line giving the predicted versus x, with the original values of y shown as red
dots.
The data at the extremes of x indicates that the relationship between y and x may be non-linear
(look at the red dots relative to the regression line at low and high values of x). We thus turn to
MARS to automatically build a model taking into account non-linearities. MARS software
constructs a model from the given x and y as follows:
ˆ y = 25
+ 6.1 max (0, x – 13)
– 3.1 max (0, 13 – x)
Figure 9.9
A Simple MARS Model of the Same Data
Figure 9.10 shows a plot of this function: the predicted versus x, with the original values of y
once again shown as red dots. The predicted response is now a better fit to the original y values.
MARS has automatically produced a kink in the predicted y to take into account non-linearity.
The kink is produced by hinge functions. The hinge functions are the expressions starting with
max (where max(a, b) is a if a > b, else b). Hinge functions are described in more detail below.
In this simple example, we can easily see from the plot that the y has a non-linear relationship
with x (and might perhaps guess that y varies with the square of x). However, in general there
will be multiple independent variables, and the relationship between y and these variables will
be unclear and not easily visible by plotting. We can use MARS to discover that non-linear
relationship.
An example MARS expression with multiple variables is ozone = 5.2
+ 0.93 max(0, temp – 58)
– 0.64 max(0, temp – 68)
196 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY