Page 132 - DCOM409_CONTEMPORARY_ACCOUNTING
P. 132
Unit 10: IFRS and its Relevance
5. Fair Value: IFRS uses fair value as a measurement base for valuing most of the items of Notes
financial statements. The use of fair value accounting can bring a lot of volatility and
subjectivity to the financial statements. It also involves a lot of hard work in arriving at
the fair value and valuation experts have to be used. Moreover, adjustments to fair value
result in gains or losses which are reflected in the income statements. Whether this can be
included in computing distributable profit is also debated.
6. Reporting Systems: The disclosure and reporting requirements under IFRS are completely
different from the Indian reporting requirements. Companies would have to ensure that
the existing business reporting model is amended to suit the reporting requirements of
IFRS. The information systems should be designed to capture new requirements related to
fixed assets, segment disclosures, related party transactions, etc. Existence of proper internal
control and minimising the risk of business disruption should be taken care of while
modifying or changing the information systems.
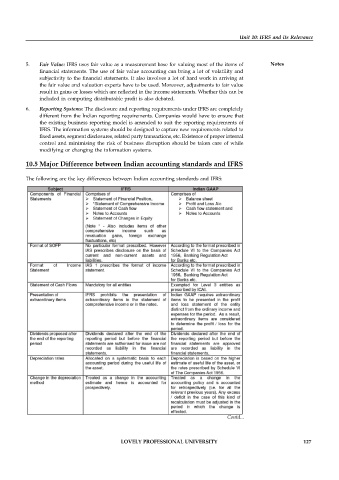
10.5 Major Difference between Indian accounting standards and IFRS
The following are the key differences between Indian accounting standards and IFRS:
Contd...
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 127