Page 213 - DCOM504_SECURITY_ANALYSIS_AND_PORTFOLIO_MANAGEMENT
P. 213
Security Analysis and Portfolio Management
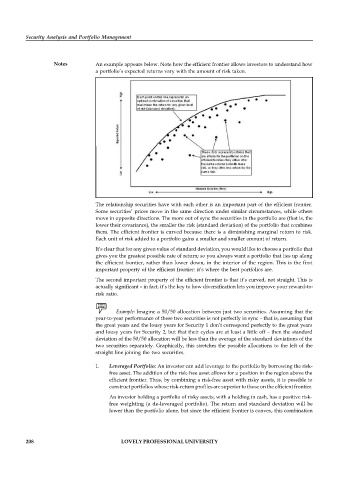
Notes An example appears below. Note how the efficient frontier allows investors to understand how
a portfolio’s expected returns vary with the amount of risk taken.
The relationship securities have with each other is an important part of the efficient frontier.
Some securities’ prices move in the same direction under similar circumstances, while others
move in opposite directions. The more out of sync the securities in the portfolio are (that is, the
lower their covariance), the smaller the risk (standard deviation) of the portfolio that combines
them. The efficient frontier is curved because there is a diminishing marginal return to risk.
Each unit of risk added to a portfolio gains a smaller and smaller amount of return.
It’s clear that for any given value of standard deviation, you would like to choose a portfolio that
gives you the greatest possible rate of return; so you always want a portfolio that lies up along
the efficient frontier, rather than lower down, in the interior of the region. This is the first
important property of the efficient frontier: it’s where the best portfolios are.
The second important property of the efficient frontier is that it’s curved, not straight. This is
actually significant – in fact, it’s the key to how diversification lets you improve your reward-to-
risk ratio.
Example: Imagine a 50/50 allocation between just two securities. Assuming that the
year-to-year performance of these two securities is not perfectly in sync – that is, assuming that
the great years and the lousy years for Security 1 don’t correspond perfectly to the great years
and lousy years for Security 2, but that their cycles are at least a little off – then the standard
deviation of the 50/50 allocation will be less than the average of the standard deviations of the
two securities separately. Graphically, this stretches the possible allocations to the left of the
straight line joining the two securities.
1. Leveraged Portfolio: An investor can add leverage to the portfolio by borrowing the risk-
free asset. The addition of the risk-free asset allows for a position in the region above the
efficient frontier. Thus, by combining a risk-free asset with risky assets, it is possible to
construct portfolios whose risk-return profiles are superior to those on the efficient frontier.
An investor holding a portfolio of risky assets, with a holding in cash, has a positive risk-
free weighting (a de-leveraged portfolio). The return and standard deviation will be
lower than the portfolio alone, but since the efficient frontier is convex, this combination
208 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY