Page 230 - DCOM504_SECURITY_ANALYSIS_AND_PORTFOLIO_MANAGEMENT
P. 230
Unit 8: Derivatives
far-off delivery dates. This is a normal contango. Conversely, normal backwardation is the Notes
result of a negative basis where nearer maturing contracts has higher futures prices than far-off
maturing contract.
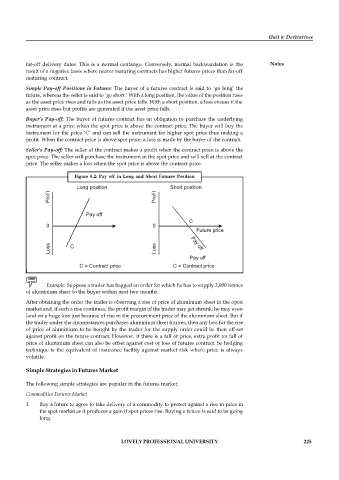
Simple Pay-off Positions in Futures: The buyer of a futures contract is said to ‘go long’ the
future, whereas the seller is said to ‘go short.’ With a long position, the value of the position rises
as the asset price rises and falls as the asset price falls. With a short position, a loss ensues if the
asset price rises but profits are generated if the asset price falls.
Buyer’s Pay-off: The buyer of futures contract has an obligation to purchase the underlying
instrument at a price when the spot price is above the contract price. The buyer will buy the
instrument for the price ‘C’ and can sell the instrument for higher spot price thus making a
profit. When the contract price is above spot price, a loss is made by the buyer of the contract.
Seller’s Pay-off: The seller of the contract makes a profit when the contract price is above the
spot price. The seller will purchase the instrument at the spot price and will sell at the contract
price. The seller makes a loss when the spot price is above the contract price.
Figure 8.2: Pay off in Long and Short Futures Position
Long position Short position
Profit Profit
Pay off
C
0 0
Future price
Loss C Loss Pay off
Pay off
C = Contract price C = Contract price
Example: Suppose a trader has bagged an order for which he has to supply 2,000 tonnes
of aluminium sheet to the buyer within next two months.
After obtaining the order the trader is observing a rise of price of aluminium sheet in the open
market and, if such a rise continues, the profit margin of the trader may get shrunk; he may even
land on a huge loss just because of rise in the procurement price of the aluminium sheet. But if
the trader under the circumstances purchases aluminium sheet futures, then any loss for the rise
of price of aluminium to be bought by the trader for the supply order could be then off-set
against profit on the future contract. However, if there is a fall of price, extra profit on fall of
price of aluminium sheet can also be offset against cost or loss of futures contract. So hedging
technique is the equivalent of insurance facility against market risk where price is always
volatile.
Simple Strategies in Futures Market
The following simple strategies are popular in the futures market:
Commodities Futures Market
1. Buy a future to agree to take delivery of a commodity to protect against a rise in price in
the spot market as it produces a gain if spot prices rise. Buying a future is said to be going
long.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 225