Page 234 - DCOM504_SECURITY_ANALYSIS_AND_PORTFOLIO_MANAGEMENT
P. 234
Unit 8: Derivatives
In most exchanges the options trading starts with European Options, as they are easy to execute Notes
and keep track of. This is the case in the BSE and the NSE. Cash settled options are those where,
the buyer is paid the difference between stock price and exercise price (call) or between exercise
price and stock price (put). Delivery settled options are those where the buyer takes delivery of
undertaking (calls) or offers delivery of the undertaking (puts).
Call Options
The following example would clarify the basics on Call Options.
A call option give the buyer the right but not the obligation to buy a given quantity of the
underlying asset, at a given price known as ‘exercise price’ or ‘strike price’ on or before a given
future date called the ‘maturity date’ or ‘expiry date’. A call option gives the buyer the right to
buy a fixed number of shares/commodities in a particular security at the exercise price up to the
date of expiration of the contract. The seller of an option is known as ‘writer.’ Unlike the buyer,
the writer has no choice regarding the fulfilment of the obligations under the contract. If the
buyer wants to exercise his right, the writer must comply. For this asymmetry of privilege, the
buyer must pay the writer the option price, which is known as ‘premium.’
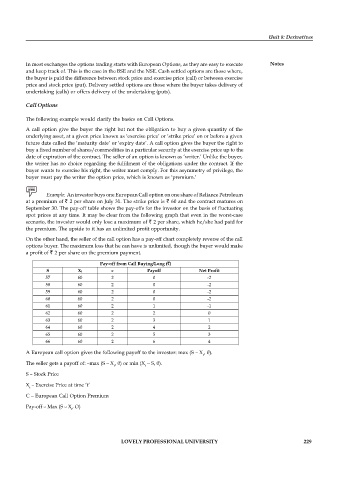
Example: An investor buys one European Call option on one share of Reliance Petroleum
at a premium of 2 per share on July 31. The strike price is 60 and the contract matures on
September 30. The pay-off table shows the pay-offs for the investor on the basis of fluctuating
spot prices at any time. It may be clear from the following graph that even in the worst-case
scenario, the investor would only lose a maximum of 2 per share, which he/she had paid for
the premium. The upside to it has an unlimited profit opportunity.
On the other hand, the seller of the call option has a pay-off chart completely reverse of the call
options buyer. The maximum loss that he can have is unlimited, though the buyer would make
a profit of 2 per share on the premium payment.
Pay-off from Call Buying/Long ( )
S Xt c Payoff Net Profit
57 60 2 0 -2
58 60 2 0 -2
59 60 2 0 -2
60 60 2 0 -2
61 60 2 1 -1
62 60 2 2 0
63 60 2 3 1
64 60 2 4 2
65 60 2 5 3
66 60 2 6 4
A European call option gives the following payoff to the investor: max (S – X , 0).
t
The seller gets a payoff of: –max (S – X , 0) or min (X – S, 0).
t t
S – Stock Price
X – Exercise Price at time ‘t’
t
C – European Call Option Premium
Pay-off – Max (S – X, O)
t
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 229