Page 238 - DCOM504_SECURITY_ANALYSIS_AND_PORTFOLIO_MANAGEMENT
P. 238
Unit 8: Derivatives
Notes
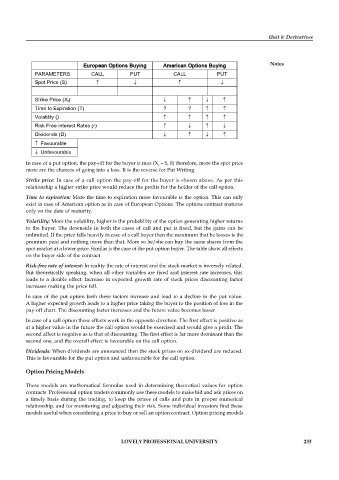
European Options Buying American Options Buying
PARAMETERS CALL PUT CALL PUT
Spot Price (S)
Strike Price (X t)
Time to Expiration (T) ? ?
Volatility ()
Risk Free Interest Rates (r)
Dividends (D)
Favourable
Unfavourable
In case of a put option, the pay-off for the buyer is max (X – S, 0) therefore, more the spot price
t
more are the chances of going into a loss. It is the reverse for Put Writing.
Strike price: In case of a call option the pay-off for the buyer is shown above. As per this
relationship a higher strike price would reduce the profits for the holder of the call option.
Time to expiration: More the time to expiration more favourable is the option. This can only
exist in case of American option as in case of European Options. The options contract matures
only on the date of maturity.
Volatility: More the volatility, higher is the probability of the option generating higher returns
to the buyer. The downside in both the cases of call and put is fixed, but the gains can be
unlimited. If the price falls heavily in case of a call buyer then the maximum that he looses is the
premium paid and nothing more than that. More so he/she can buy the same shares from the
spot market at a lower price. Similar is the case of the put option buyer. The table show all effects
on the buyer side of the contract
Risk-free rate of interest: In reality the rate of interest and the stock market is inversely related.
But theoretically speaking, when all other variables are fixed and interest rate increases, this
leads to a double effect: Increase in expected growth rate of stock prices discounting factor
increases making the price fall.
In case of the put option both these factors increase and lead to a decline in the put value.
A higher expected growth leads to a higher price taking the buyer to the position of loss in the
pay-off chart. The discounting factor increases and the future value becomes lesser
In case of a call option these effects work in the opposite direction. The first effect is positive as
at a higher value in the future the call option would be exercised and would give a profit. The
second affect is negative as is that of discounting. The first effect is far more dominant than the
second one, and the overall effect is favourable on the call option.
Dividends: When dividends are announced then the stock prices on ex-dividend are reduced.
This is favourable for the put option and unfavourable for the call option.
Option Pricing Models
These models are mathematical formulas used in determining theoretical values for option
contracts. Professional option traders commonly use these models to make bid and ask prices on
a timely basis during the trading, to keep the prices of calls and puts in proper numerical
relationship, and for monitoring and adjusting their risk. Some individual investors find these
models useful when considering a price to buy or sell an option contract. Option pricing models
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 233