Page 342 - DCOM504_SECURITY_ANALYSIS_AND_PORTFOLIO_MANAGEMENT
P. 342
Unit 14: Portfolio Revision
portfolio? Or, will it be set pre-specified period of time or percentage change in some Notes
economic or market index or percentage change in the value of the aggressive portfolio?
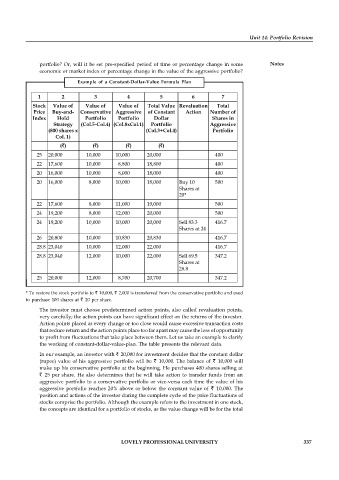
Example of a Constant-Dollar-Value Formula Plan
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Stock Value of Value of Value of Total Value Revaluation Total
Price Buy-and- Conservative Aggressive of Constant Action Number of
Index Hold Portfolio Portfolio Dollar Shares in
Strategy (Col.5-Col.4) (Col.8xCol.1) Portfolio Aggressive
(800 shares x (Col.3+Col.4) Portfolio
Col. 1)
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
25 20,000 10,000 10,000 20,000 400
22 17,600 10,000 8,800 18,800 400
20 16,000 10,000 8,000 18,000 400
20 16,000 8,000 10,000 18,000 Buy 10 500
Shares at
20*
22 17,600 8,000 11,000 19,000 500
24 19,200 8,000 12,000 20,000 500
24 19,200 10,000 10,000 20,000 Sell 83.3 416.7
Shares at 24
26 20,800 10,000 10,830 20,830 416.7
28.8 23,040 10,000 12,000 22,000 416.7
28.8 23,040 12,000 10,000 22,000 Sell 69.5 347.2
Shares at
28.8
25 20,000 12,000 8,700 20,700 347.2
* To restore the stock portfolio to 10,000, 2,000 is transferred from the conservative portfolio and used
to purchase 100 shares at 20 per share.
The investor must choose predetermined action points, also called revaluation points,
very carefully; the action points can have significant effect on the returns of the investor.
Action points placed at every change or too close would cause excessive transaction costs
that reduce return and the action points place too far apart may cause the loss of opportunity
to profit from fluctuations that take place between them. Let us take an example to clarify
the working of constant-dollar-value-plan. The table presents the relevant data.
In our example, an investor with 20,000 for investment decides that the constant dollar
(rupee) value of his aggressive portfolio will be 10,000. The balance of 10,000 will
make up his conservative portfolio at the beginning. He purchases 400 shares selling at
25 per share. He also determines that he will take action to transfer funds from an
aggressive portfolio to a conservative portfolio or vice-versa each time the value of his
aggressive portfolio reaches 20% above or below the constant value of 10,000. The
position and actions of the investor during the complete cycle of the price fluctuations of
stocks comprise the portfolio. Although the example refers to the investment in one stock,
the concepts are identical for a portfolio of stocks, as the value change will be for the total
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 337