Page 233 - DCOM508_CORPORATE_TAX_PLANNING
P. 233
Corporate Tax Planning
Notes
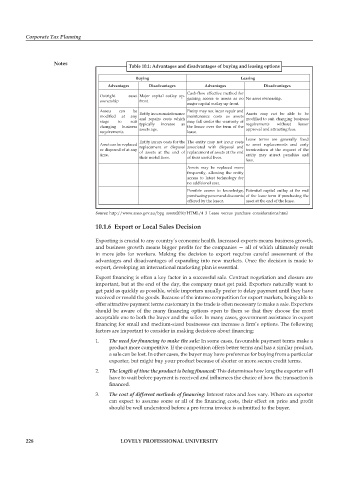
Table 10.1: Advantages and disadvantages of buying and leasing options
Buying Leasing
Advantages Disadvantages Advantages Disadvantages
Cash-flow effective method for
Outright asset Major capital outlay up-
ownership front. gaining access to assets as no No asset ownership.
major capital outlay up-front.
Assets can be Entity may not incur repair and
modifi ed at any Entity incurs maintenance maintenance costs as assets Assets may not be able to be
stage to suit and repairs costs which may fall under the warranty of modified to suit changing business
changing business typically increase as the lessor over the term of the requirements without lessor
requirements. assets age. lease. approval and attracting fees.
Lease terms are generally fi xed
Entity incurs costs for the The entity may not incur costs
Asset can be replaced replacement or disposal associated with disposal and so asset replacements and early
or disposed of at any of assets at the end of replacement of assets at the end terminations at the request of the
time. entity may attract penalties and
their useful lives. of their useful lives.
fees.
Assets may be replaced more
frequently, allowing the entity
access to latest technology for
no additional cost.
Possible access to knowledge, Potential capital outlay at the end
purchasing power and discounts of the lease term if purchasing the
offered by the lessor. asset at the end of the lease.
Source: http://www.anao.gov.au/bpg_assets2010/HTML/4_3_Lease_versus_purchase_considerations.html
10.1.6 Export or Local Sales Decision
Exporting is crucial to any country’s economic health. Increased exports means business growth,
and business growth means bigger profits for the companies — all of which ultimately result
in more jobs for workers. Making the decision to export requires careful assessment of the
advantages and disadvantages of expanding into new markets. Once the decision is made to
export, developing an international marketing plan is essential.
Export financing is often a key factor in a successful sale. Contract negotiation and closure are
important, but at the end of the day, the company must get paid. Exporters naturally want to
get paid as quickly as possible, while importers usually prefer to delay payment until they have
received or resold the goods. Because of the intense competition for export markets, being able to
offer attractive payment terms customary in the trade is often necessary to make a sale. Exporters
should be aware of the many financing options open to them so that they choose the most
acceptable one to both the buyer and the seller. In many cases, government assistance in export
financing for small and medium-sized businesses can increase a firm’s options. The following
factors are important to consider in making decisions about fi nancing:
1. The need for financing to make the sale: In some cases, favourable payment terms make a
product more competitive. If the competition offers better terms and has a similar product,
a sale can be lost. In other cases, the buyer may have preference for buying from a particular
exporter, but might buy your product because of shorter or more secure credit terms.
2. The length of time the product is being fi nanced: This determines how long the exporter will
have to wait before payment is received and influences the choice of how the transaction is
fi nanced.
3. The cost of different methods of fi nancing: Interest rates and fees vary. Where an exporter
can expect to assume some or all of the financing costs, their effect on price and profi t
should be well understood before a pro forma invoice is submitted to the buyer.
228 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY