Page 122 - DCOM510_FINANCIAL_DERIVATIVES
P. 122
Unit 7: Application of Futures Contracts
Notes
Case Study Using Currency Futures for Hedging
M has to pay €10m in three months for a delivery of parts from Germany invoiced
in euro’s. Worried? Over the next three months: $ ............ and € ............. For example,
Gsuppose the spot ex-rate is $1.25/€ and remains constant for 3 months, the parts
will cost $12,500,000 ($1.25/€ x €10m). If the euro appreciates by 4% over the next three
months, the ex-rate will be ............ and the parts will now cost ............, an increase of
.............
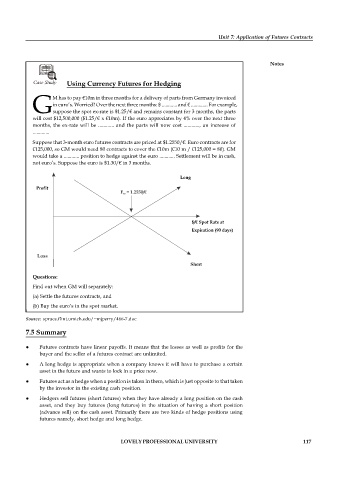
Suppose that 3-month euro futures contracts are priced at $1.2550/€. Euro contracts are for
€125,000, so GM would need 80 contracts to cover the €10m (€10 m / €125,000 = 80). GM
would take a ............ position to hedge against the euro ............ Settlement will be in cash,
not euro’s. Suppose the euro is $1.30/€ in 3 months.
Long
Profit
F = 1.2550/€
90
$/€ Spot Rate at
Expiration (90 days)
Loss
Short
Questions:
Find out when GM will separately:
(a) Settle the futures contracts, and
(b) Buy the euro’s in the spot market.
Source: spruce.flint.umich.edu/~mjperry/466-7.doc
7.5 Summary
Futures contracts have linear payoffs. It means that the losses as well as profits for the
buyer and the seller of a futures contract are unlimited.
A long hedge is appropriate when a company knows it will have to purchase a certain
asset in the future and wants to lock in a price now.
Futures act as a hedge when a position is taken in them, which is just opposite to that taken
by the investor in the existing cash position.
Hedgers sell futures (short futures) when they have already a long position on the cash
asset, and they buy futures (long futures) in the situation of having a short position
(advance sell) on the cash asset. Primarily there are two kinds of hedge positions using
futures namely, short hedge and long hedge.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 117