Page 131 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 131
Digital Circuits and Logic Design
Notes • Transistor-Transistor Logic refers to the technology for designing and fabricating digital
integrated circuits that employ logic gates consisting primarily of bipolar transistors.
• The major problem with NMOS is that a DC current must flow through a logic gate even
when the output is in a steady state.
7.9 Keywords
Direct-Coupled Transistor Logic (DCTL) Gate: A DCTL gate is one wherein the bases of the
transistors are connected directly to inputs without any base resistors.
High Threshold Logic (HTL): HTL is a variant of DTL which is used in such environments where
noise is very high. It incorporates Zener diodes to create a large offset between logic 1 and logic
0 voltage levels
Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect-Transistor (MOSFET): A MOSFET can be made to
operate as a resistor, so the whole circuit can be made with n-channel MOSFETs only.
Positive Emitter-Coupled Logic (PECL): PECL is a further development of ECL using a positive
5V supply instead of a negative 5V supply.
Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL): TTL refers to the technology for designing and fabricating
digital integrated circuits that employ logic gates consisting primarily of bipolar transistors.
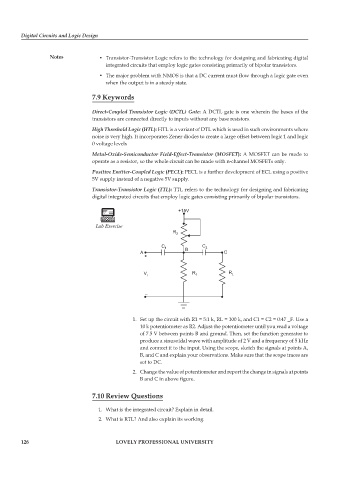
1. Set up the circuit with R1 = 5:1 k, RL = 100 k, and C1 = C2 = 0:47 _F. Use a
10 k potentiometer as R2. Adjust the potentiometer until you read a voltage
of 7.5 V between points B and ground. Then, set the function generator to
produce a sinusoidal wave with amplitude of 2 V and a frequency of 5 kHz
and connect it to the input. Using the scope, sketch the signals at points A,
B, and C and explain your observations. Make sure that the scope traces are
set to DC.
2. Change the value of potentiometer and report the change in signals at points
B and C in above figure.
7.10 Review Questions
1. What is the integrated circuit? Explain in detail.
2. What is RTL? And also explain its working.
126 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY