Page 62 - DCAP210_INTRODUCTION__TO_MICROPROCESSORS
P. 62
Introduction to Microprocessors
Notes the IBM PC. Since the original processor used in an IBM PC was based upon the Intel 8086
microprocessor, successive microprocessors using the same set of instructions to run have been
named similarly—the 80286, 80386 and 80486, for example.
A microprocessor using x64 architecture is slightly different than the x86 processor. An x64
processor is capable of processing not only 32-bit instructions but also 64-bit instructions as well.
Because of the increased capability of the x64 microprocessor, a computer that utilizes an x64
microprocessor is also capable of utilizing more memory (128 GB maximum vs. 4 GB maximum)
than a computer with an x86 microprocessor.
An x64 microprocessor, therefore, would be the better choice if you plan to use the computer for
memory-intensive applications, or if you need better overall performance out of your computer
system.
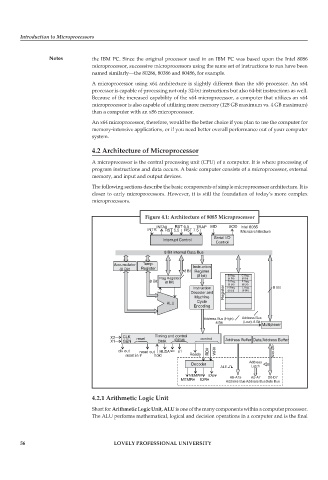
4.2 Architecture of Microprocessor
A microprocessor is the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer. It is where processing of
program instructions and data occurs. A basic computer consists of a microprocessor, external
memory, and input and output devices.
The following sections describe the basic components of simple microprocessor architecture. It is
closer to early microprocessors. However, it is still the foundation of today’s more complex
microprocessors.
Figure 4.1: Architecture of 8085 Microprocessor
4.2.1 Arithmetic Logic Unit
Short for Arithmetic Logic Unit, ALU is one of the many components within a computer processor.
The ALU performs mathematical, logical and decision operations in a computer and is the final
56 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY