Page 261 - DCAP310_INTRODUCTION_TO_ARTIFICIAL_INTELLIGENCE_AND_EXPERT_SYSTEMS
P. 261
Unit 14: Types of Learning
Once a universal (class) has been identified, then the next step in the acquisition of knowledge is Notes
the abstraction of the intension, which is the particular, the species, or the connotation.
Connotation as its meaning as particular is “the assertion that at least one member of one class of things
is either included or excluded as a member of some other class.” This means, for example, that a poodle
is the particular in a class or universal concept called “dog” or “canine”.
Some of the most important issues in knowledge acquisition are as follows:
Most knowledge is in the heads of experts
Experts have vast amounts of knowledge
Experts have a lot of tacit knowledge
They don’t know all that they know and use
Tacit knowledge is hard (impossible) to describe
Experts are very busy and valuable people
Each expert doesn’t know everything
Knowledge has a “shelf life”
Self Assessment
State whether the following statements are true or false:
1. Perception is the recognition within the knowing subject of the event of having had a
sensation.
2. Knowledge acquisition is not a method of learning.
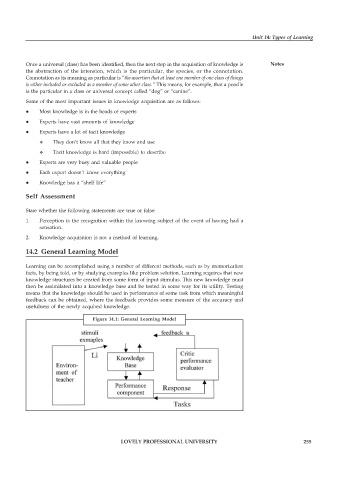
14.2 General Learning Model
Learning can be accomplished using a number of different methods, such as by memorization
facts, by being told, or by studying examples like problem solution. Learning requires that new
knowledge structures be created from some form of input stimulus. This new knowledge must
then be assimilated into a knowledge base and be tested in some way for its utility. Testing
means that the knowledge should be used in performance of some task from which meaningful
feedback can be obtained, where the feedback provides some measure of the accuracy and
usefulness of the newly acquired knowledge.
Figure 14.1: General Learning Model
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 255