Page 33 - DCAP313_LAB_ON_COMPUTER_GRAPHICS
P. 33
Unit 2: Graphics Systems
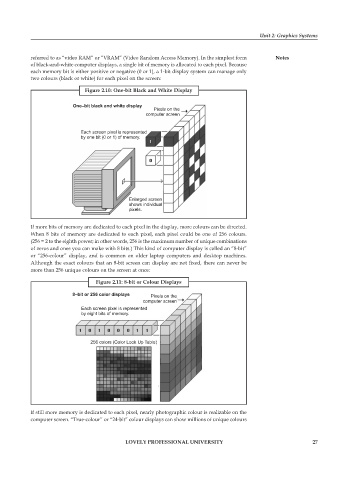
referred to as “video RAM” or “VRAM” (Video Random Access Memory). In the simplest form Notes
of black-and-white computer displays, a single bit of memory is allocated to each pixel. Because
each memory bit is either positive or negative (0 or 1), a 1-bit display system can manage only
two colours (black or white) for each pixel on the screen:
Figure 2.10: One-bit Black and White Display
If more bits of memory are dedicated to each pixel in the display, more colours can be directed.
When 8 bits of memory are dedicated to each pixel, each pixel could be one of 256 colours.
(256 = 2 to the eighth power; in other words, 256 is the maximum number of unique combinations
of zeros and ones you can make with 8 bits.) This kind of computer display is called an “8-bit”
or “256-colour” display, and is common on older laptop computers and desktop machines.
Although the exact colours that an 8-bit screen can display are not fixed, there can never be
more than 256 unique colours on the screen at once:
Figure 2.11: 8-bit or Colour Displays
If still more memory is dedicated to each pixel, nearly photographic colour is realizable on the
computer screen. “True-colour” or “24-bit” colour displays can show millions of unique colours
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 27