Page 41 - DCAP313_LAB_ON_COMPUTER_GRAPHICS
P. 41
Unit 3: Implementing Line Algorithm
applied. A typical flat-bed plotter uses two of these motors, one for the x-axis and a second for Notes
the y-axis, to control the position of a pen over a sheet of paper. A solenoid is used to raise and
lower the actual pen when drawing and positioning.
3.1 Concept of Implementing Line Algorithm
The essential “line drawing” algorithm used in computer graphics is Bresenham’s Algorithm.
This algorithm was developed to draw lines on digital plotters, but has found broad-spread
usage in computer graphics. The algorithm is fast it can be applied with integer computations
only and very easy to explain.
The following types of implementing line algorithm are:
1. Bresenham’s Line Algorithm
2. DDA Line Algorithm
3.2 Concept of Bresenham’s Algorithm
The Bresenham Algorithm for drawing lines on the discrete plane, for instance computer monitor
is one of the primary algorithms in computer graphics.
3.2.1 Bresenham’s Algorithm
The Bresenham line algorithm is an algorithm which decides which points in an n-dimensional
raster should be plotted so as to form a close approximation to a straight line between two
given points. It is commonly used to draw lines on a computer screen, as it uses only integer
addition, subtraction and bit shifting, all of which are very cheap operations in standard computer
architectures. It is one of the initial algorithms developed in the field of computer graphics.
A minor extension to the original algorithm also deals with drawing circles.
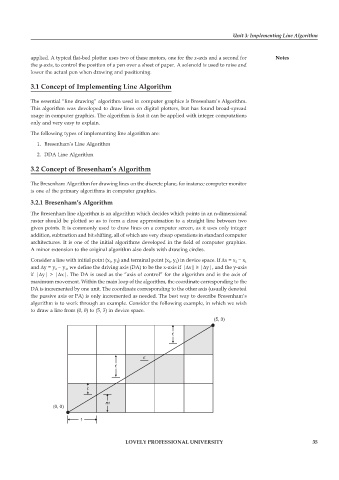
Consider a line with initial point (x 1 , y 1 ) and terminal point (x 2 , y 2 ) in device space. If ∆x = x 2 − x 1
and ∆y = y 2 − y 1 , we define the driving axis (DA) to be the x-axis if |∆x| ≥ |∆y|, and the y-axis
if |∆y| > |∆x|. The DA is used as the “axis of control” for the algorithm and is the axis of
maximum movement. Within the main loop of the algorithm, the coordinate corresponding to the
DA is incremented by one unit. The coordinate corresponding to the other axis (usually denoted
the passive axis or PA) is only incremented as needed. The best way to describe Bresenham’s
algorithm is to work through an example. Consider the following example, in which we wish
to draw a line from (0, 0) to (5, 3) in device space.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 35