Page 45 - DCAP313_LAB_ON_COMPUTER_GRAPHICS
P. 45
Unit 3: Implementing Line Algorithm
Notes
If we consider the lower-left-hand corner of the grid to be (0, 0), then it is simply seen that the
early is:
Ê
1
Œ =- 1 - y 1 - D y( 1 D - x ) ˆ ˜ ¯
Á
Ë
x
We now utilize this to modify Bresenham’s algorithm accordingly.
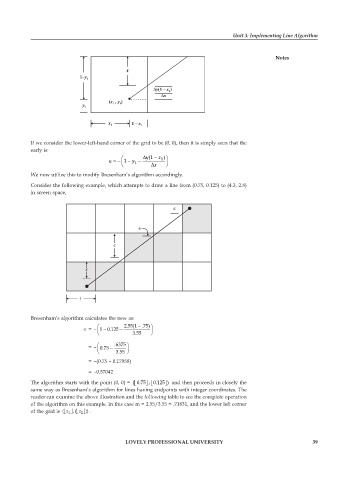
Consider the following example, which attempts to draw a line from (0.75, 0.125) to (4.3, 2.8)
in screen space,
Bresenham’s algorithm calculates the new as:
.(
Ê
= – 1 - 0 125 - 2551 - . 75 ˆ ) ˜ ¯
.
Á
Ë
355
.
Ê
= – 075 - . 6375ˆ ˜
.
Á
Ë
355 ¯
.
= –(0.75 – 0.17958)
= –0.57042
, 0
)
The algorithm starts with the point (0, 0) = (.075˙ ˚ Í Î .125˙ ˚ and then proceeds in closely the
Í Î
same way as Bresenham’s algorithm for lines having endpoints with integer coordinates. The
reader can examine the above illustration and the following table to see the complete operation
of the algorithm on this example. In this case m = 2.55/3.55 = .71831, and the lower left corner
of the grid is ( z Í Î 1 ˙ ˚ , ( z Í Î 2 ˙ ˚ )) .
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 39