Page 187 - DCAP208_Management Support Systems
P. 187
Management Support Systems
Notes
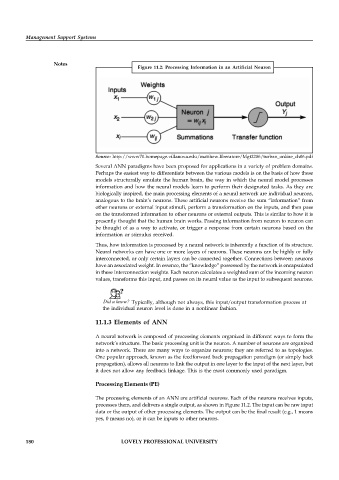
Figure 11.2: Processing Information in an Artificial Neuron
Source: http://www70.homepage.villanova.edu/matthew.liberatore/Mgt2206/turban_online_ch06.pdf
Several ANN paradigms have been proposed for applications in a variety of problem domains.
Perhaps the easiest way to differentiate between the various models is on the basis of how these
models structurally emulate the human brain, the way in which the neural model processes
information and how the neural models learn to perform their designated tasks. As they are
biologically inspired, the main processing elements of a neural network are individual neurons,
analogous to the brain’s neurons. These artificial neurons receive the sum “information” from
other neurons or external input stimuli, perform a transformation on the inputs, and then pass
on the transformed information to other neurons or external outputs. This is similar to how it is
presently thought that the human brain works. Passing information from neuron to neuron can
be thought of as a way to activate, or trigger a response from certain neurons based on the
information or stimulus received.
Thus, how information is processed by a neural network is inherently a function of its structure.
Neural networks can have one or more layers of neurons. These neurons can be highly or fully
interconnected, or only certain layers can be connected together. Connections between neurons
have an associated weight. In essence, the “knowledge” possessed by the network is encapsulated
in these interconnection weights. Each neuron calculates a weighted sum of the incoming neuron
values, transforms this input, and passes on its neural value as the input to subsequent neurons.
Did u know? Typically, although not always, this input/output transformation process at
the individual neuron level is done in a nonlinear fashion.
11.1.3 Elements of ANN
A neural network is composed of processing elements organized in different ways to form the
network’s structure. The basic processing unit is the neuron. A number of neurons are organized
into a network. There are many ways to organize neurons; they are referred to as topologies.
One popular approach, known as the feedforward back propagation paradigm (or simply back
propagation), allows all neurons to link the output in one layer to the input of the next layer, but
it does not allow any feedback linkage. This is the most commonly used paradigm.
Processing Elements (PE)
The processing elements of an ANN are artificial neurons. Each of the neurons receives inputs,
processes them, and delivers a single output, as shown in Figure 11.2. The input can be raw input
data or the output of other processing elements. The output can be the final result (e.g., 1 means
yes, 0 means no), or it can be inputs to other neurons.
180 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY