Page 189 - DCAP208_Management Support Systems
P. 189
Management Support Systems
Notes Outputs: The outputs of a network contain the solution to a problem.
Example: In the case of a loan application, the outputs can be yes or no.
The ANN assigns numeric values to the outputs, such as 1 for yes and 0 for no. The purpose of the
network is to compute the values of the output. Often, post-processing of the outputs is required
because some networks use two outputs: one for yes and another for no. It is common to have to
round the outputs to the nearest 0 or 1.
Connection Weights: Connection weights are the key elements in an ANN. They express the
relative strength (or mathematical value) of the input data or the many connections that transfer
data from layer to layer. In other words, weights express the relative importance of each input
to a processing element and, ultimately, the outputs weights are crucial in that they store
learned patterns of information. It is through repeated adjustments of weights that a network
learns.
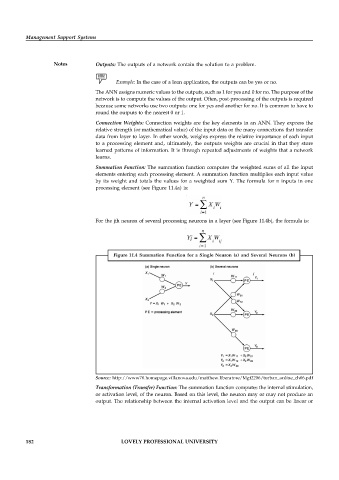
Summation Function: The summation function computes the weighted sums of all the input
elements entering each processing element. A summation function multiplies each input value
by its weight and totals the values for a weighted sum Y. The formula for n inputs in one
processing element (see Figure 11.4a) is:
For the jth neuron of several processing neurons in a layer (see Figure 11.4b), the formula is:
Figure 11.4 Summation Function for a Single Neuron (a) and Several Neurons (b)
Source: http://www70.homepage.villanova.edu/matthew.liberatore/Mgt2206/turban_online_ch06.pdf
Transformation (Transfer) Function: The summation function computes the internal stimulation,
or activation level, of the neuron. Based on this level, the neuron may or may not produce an
output. The relationship between the internal activation level and the output can be linear or
182 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY