Page 191 - DCAP208_Management Support Systems
P. 191
Management Support Systems
Notes
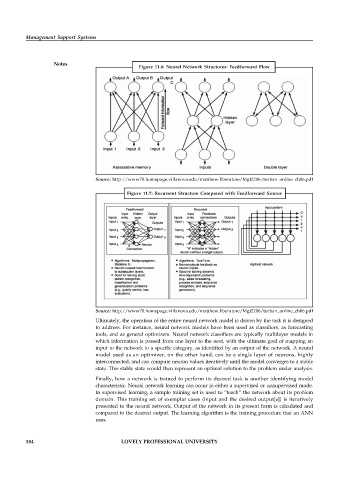
Figure 11.6: Neural Network Structures: Feedforward Flow
Source: http://www70.homepage.villanova.edu/matthew.liberatore/Mgt2206/turban_online_ch06.pdf
Figure 11.7: Recurrent Structure Compared with Feedforward Source
Source: http://www70.homepage.villanova.edu/matthew.liberatore/Mgt2206/turban_online_ch06.pdf
Ultimately, the operation of the entire neural network model is driven by the task it is designed
to address. For instance, neural network models have been used as classifiers, as forecasting
tools, and as general optimizers. Neural network classifiers are typically multilayer models in
which information is passed from one layer to the next, with the ultimate goal of mapping an
input to the network to a specific category, as identified by an output of the network. A neural
model used as an optimizer, on the other hand, can be a single layer of neurons, highly
interconnected, and can compute neuron values iteratively until the model converges to a stable
state. This stable state would then represent an optimal solution to the problem under analysis.
Finally, how a network is trained to perform its desired task is another identifying model
characteristic. Neural network learning can occur in either a supervised or unsupervised mode.
In supervised learning, a sample training set is used to “teach” the network about its problem
domain. This training set of exemplar cases (input and the desired output[s]) is iteratively
presented to the neural network. Output of the network in its present form is calculated and
compared to the desired output. The learning algorithm is the training procedure that an ANN
uses.
184 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY