Page 61 - DCAP208_Management Support Systems
P. 61
Management Support Systems
Notes a decision is implemented, the results usually occur in the future. Whereas DSS are typically
designed to determine what will be, traditional MIS report what is or what was. There is
no point in running a what-if (sensitivity) analysis on the past because decisions made
then have no impact in the future. Forecasting is getting easier as software vendors automate
many of the complications of developing such models.
Notes Forecasting system that incorporates its predictive analytics technology is ideally
for retailers. This software is more automated than most other forecasting packages.
4. Multiple Models: A DSS can include several models which represents a different part of the
decision-making problem.
Example: P&G supply-chain DSS includes a location model to locate distribution center,
a product-strategy model, a demand-forecasting model, a cost generation model, a financial-
and risk-simulation model, and even a GIS model.
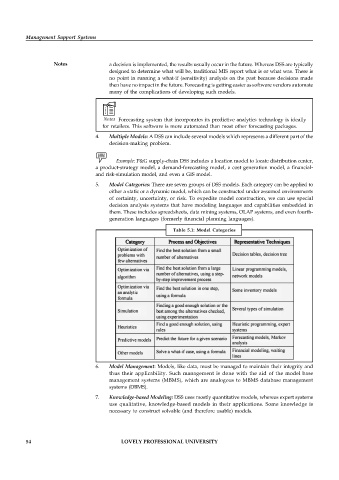
5. Model Categories: There are seven groups of DSS models. Each category can be applied to
either a static or a dynamic model, which can be constructed under assumed environments
of certainty, uncertainty, or risk. To expedite model construction, we can use special
decision analysis systems that have modeling languages and capabilities embedded in
them. These includes spreadsheets, data mining systems, OLAP systems, and even fourth-
generation languages (formerly financial planning languages).
Table 5.1: Model Categories
6. Model Management: Models, like data, must be managed to maintain their integrity and
thus their applicability. Such management is done with the aid of the model base
management systems (MBMS), which are analogous to MBMS database management
systems (DBMS).
7. Knowledge-based Modeling: DSS uses mostly quantitative models, whereas expert systems
use qualitative, knowledge-based models in their applications. Some knowledge is
necessary to construct solvable (and therefore usable) models.
54 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY