Page 122 - DCAP201_FUNDAMENTALS_OF_DATA_STRUCTURES
P. 122
Unit 8: Operations on Linked List
Notes
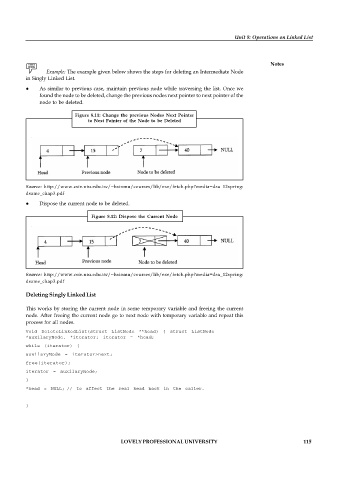
Example: The example given below shows the steps for deleting an Intermediate Node
in Singly Linked List.
As similar to previous case, maintain previous node while traversing the list. Once we
found the node to be deleted, change the previous nodes next pointer to next pointer of the
node to be deleted.
Figure 8.11: Change the previous Nodes Next Pointer
to Next Pointer of the Node to be Deleted
Source: http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~hsinmu/courses/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=dsa_12spring:
dsame_chap3.pdf
Dispose the current node to be deleted.
Figure 8.12: Dispose the Current Node
Source: http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~hsinmu/courses/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=dsa_12spring:
dsame_chap3.pdf
Deleting Singly Linked List
This works by storing the current node in some temporary variable and freeing the current
node. After freeing the current node go to next node with temporary variable and repeat this
process for all nodes.
Void DeleteLinkedList(struct ListNode **head) { struct ListNode
*auxilaryNode, *iterator; iterator = *head;
while (iterator) {
auxilaryNode = iterator>next;
free(iterator);
iterator = auxilaryNode;
}
*head = NULL; // to affect the real head back in the caller.
}
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 115