Page 125 - DCAP201_FUNDAMENTALS_OF_DATA_STRUCTURES
P. 125
Fundamentals of Data Structures
Notes
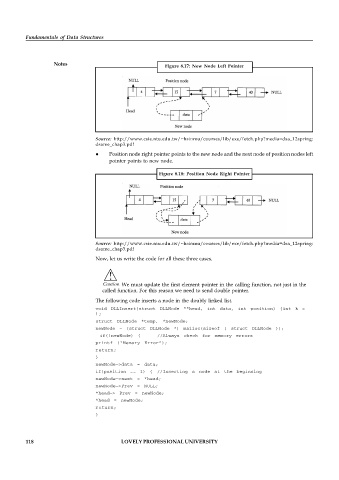
Figure 8.17: New Node Left Pointer
Source: http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~hsinmu/courses/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=dsa_12spring:
dsame_chap3.pdf
Position node right pointer points to the new node and the next node of position nodes left
pointer points to new node.
Figure 8.18: Position Node Right Pointer
Source: http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~hsinmu/courses/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=dsa_12spring:
dsame_chap3.pdf
Now, let us write the code for all these three cases.
!
Caution We must update the first element pointer in the calling function, not just in the
called function. For this reason we need to send double pointer.
The following code inserts a node in the doubly linked list.
void DLLInsert(struct DLLNode **head, int data, int position) {int k =
1;
struct DLLNode *temp, *newNode;
newNode = (struct DLLNode *) malloc(sizeof ( struct DLLNode ));
if(!newNode) { //Always check for memory errors
printf (“Memory Error”);
return;
}
newNode—>data = data;
if(position == 1) { //Inserting a node at the beginning
newNode—>next = *head;
newNode—>Prev = NULL;
*head—> Prev = newNode;
*head = newNode;
return;
}
118 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY