Page 243 - DCAP312_WEB_TECHNOLOGIES_II
P. 243
Unit 12: Security and Membership
ASP.NET works in concert with the Microsoft .NET Framework and Internet Information Services Notes
(IIS) to help provide Web application protection. To help protect an ASP.NET application, you
must perform the two fundamental functions described in the Table 12.1.
Table 12.1: Security Function
Security function Description
Authentication in Assures that the user is, in fact, who the user claims to be. The
ASP.NET application obtains credentials (various forms of identification, such
as name and password) from a user and validates those credentials
against some authority. If the credentials are valid, the entity that
submitted the credentials is considered an authenticated identity.
Authorization in Limits access rights by granting or denying specific permissions to
ASP.NET an authenticated identity.
IIS can also grant or deny access based on a user’s host name or IP address. Any further access
authorization is performed by NTFS file access permission’s URL authorization.
It is helpful to understand how all the various security subsystems interact. Since ASP.NET is
built on the Microsoft .NET Framework, the ASP.NET application developer also has access
to all the built-in security features of the .NET Framework, such as code access security and
role-based user-access security. For details about the security capabilities of ASP.NET, see ASP.
NET code access security.
Write the steps to activate IIS server.
12.1.2 ASP.NET Infrastructure and Subsystem Relationships, as Related to
Security
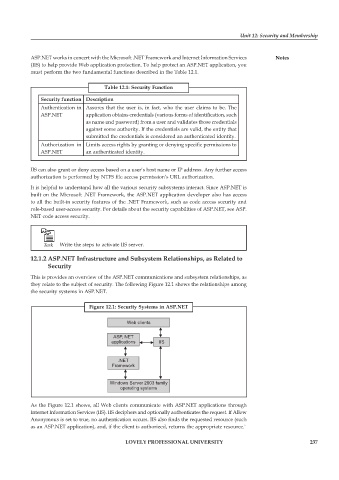
This is provides an overview of the ASP.NET communications and subsystem relationships, as
they relate to the subject of security. The following Figure 12.1 shows the relationships among
the security systems in ASP.NET.
Figure 12.1: Security Systems in ASP.NET
Web clients
ASP, NET
applications IIS
.NET
Framework
Windows Server 2003 family
operating systems
As the Figure 12.1 shows, all Web clients communicate with ASP.NET applications through
Internet Information Services (IIS). IIS deciphers and optionally authenticates the request. If Allow
Anonymous is set to true, no authentication occurs. IIS also finds the requested resource (such
as an ASP.NET application), and, if the client is authorized, returns the appropriate resource.`
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 237