Page 128 - DCAP601_SIMULATION_AND_MODELING
P. 128
Simulation and Modelling
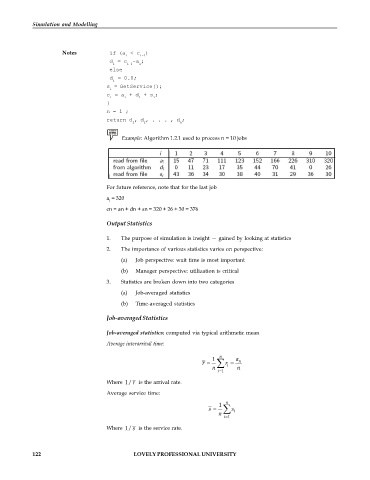
Notes if (a < c )
i i–1
d = c –a ;
i i–1 i
else
d = 0.0;
i
s = GetService();
i
c = a + d + s ;
i i i i
}
n = i ;
return d , d , . . . , d ;
1 2 n
Example: Algorithm 1.2.1 used to process n = 10 jobs
For future reference, note that for the last job
a = 320
i
cn = an + dn + sn = 320 + 26 + 30 = 376
Output Statistics
1. The purpose of simulation is insight — gained by looking at statistics
2. The importance of various statistics varies on perspective:
(a) Job perspective: wait time is most important
(b) Manager perspective: utilization is critical
3. Statistics are broken down into two categories
(a) Job-averaged statistics
(b) Time-averaged statistics
Job-averaged Statistics
Job-averaged statistics: computed via typical arithmetic mean
Average interarrival time:
n
1 a n
r r
i
n n
i 1
Where 1/r is the arrival rate.
Average service time:
n
1
s s i
n
i 1
Where 1/ s is the service rate.
122 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY