Page 146 - DCAP605_ADVANCED_DATA_STRUCTURE_AND_ALGORITHMS
P. 146
Unit 6: Binary Search Tree and AVL Trees
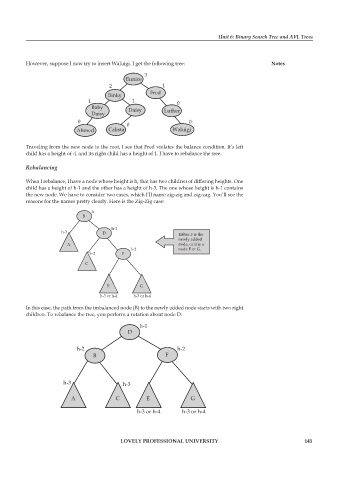
However, suppose I now try to insert Waluigi. I get the following tree: Notes
3
Eunice
2 1
Fred
Binky
1 1 0
Baby Daisy
Daisy Luther
0 0
0
Ahmed Calista Waluigi
Traveling from the new node to the root, I see that Fred violates the balance condition. It’s left
child has a height of -1 and its right child has a height of 1. I have to rebalance the tree.
Rebalancing
When I rebalance, I have a node whose height is h, that has two children of differing heights. One
child has a height of h-1 and the other has a height of h-3. The one whose height is h-1 contains
the new node. We have to consider two cases, which I’ll name zig-zig and zig-zag. You’ll see the
reasons for the names pretty clearly. Here is the Zig-Zig case:
h
B
h-1
h-3 D Either F is the
newly added
A node, or it is a
h-2 node E or G.
h-2 F
C
E G
h-3 or h-4 h-3 or h-4
In this case, the path from the imbalanced node (B) to the newly added node starts with two right
children. To rebalance the tree, you perform a rotation about node D:
h-1
D
h-2 h-2
B F
h-3 h-3
A C E G
h-3 or h-4 h-3 or h-4
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 141