Page 38 - DCAP605_ADVANCED_DATA_STRUCTURE_AND_ALGORITHMS
P. 38
Unit 2: Linked Lists
{ Notes
prev -> link = curr -> link ;
free ( curr );
}
}
}
return(p);
}
/* a function to compute the length of a linked list */
int length ( struct node *p )
{
int count = 0 ;
while ( p != NULL )
{
count++;
p = p->link;
}
return ( count ) ;
}
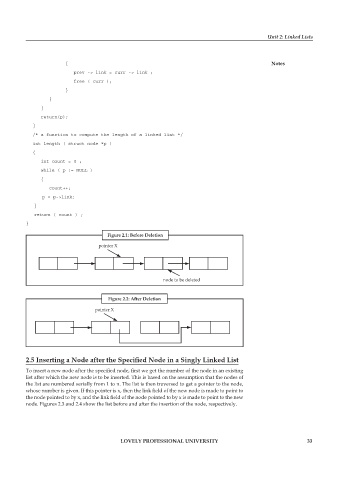
Figure 2.1: Before Deletion
pointer X
node to be deleted
Figure 2.2: After Deletion
pointer X
2.5 Inserting a Node after the Specified Node in a Singly Linked List
To insert a new node after the specifi ed node, first we get the number of the node in an existing
list after which the new node is to be inserted. This is based on the assumption that the nodes of
the list are numbered serially from 1 to n. The list is then traversed to get a pointer to the node,
whose number is given. If this pointer is x, then the link field of the new node is made to point to
the node pointed to by x, and the link field of the node pointed to by x is made to point to the new
node. Figures 2.3 and 2.4 show the list before and after the insertion of the node, respectively.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 33