Page 42 - DCAP605_ADVANCED_DATA_STRUCTURE_AND_ALGORITHMS
P. 42
Unit 2: Linked Lists
Notes
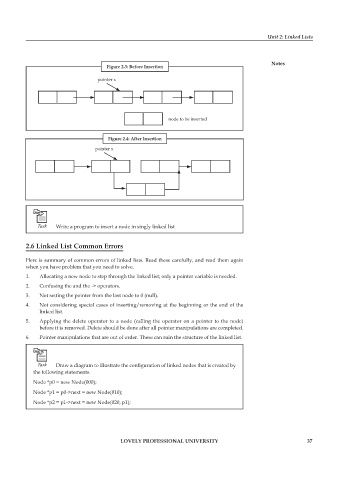
Figure 2.3: Before Insertion
pointer x
node to be inserted
Figure 2.4: After Insertion
pointer x
Task Write a program to insert a node in singly linked list
2.6 Linked List Common Errors
Here is summary of common errors of linked lists. Read these carefully, and read them again
when you have problem that you need to solve.
1. Allocating a new node to step through the linked list; only a pointer variable is needed.
2. Confusing the and the -> operators.
3. Not setting the pointer from the last node to 0 (null).
4. Not considering special cases of inserting/removing at the beginning or the end of the
linked list.
5. Applying the delete operator to a node (calling the operator on a pointer to the node)
before it is removed. Delete should be done after all pointer manipulations are completed.
6. Pointer manipulations that are out of order. These can ruin the structure of the linked list.
Task Draw a diagram to illustrate the configuration of linked nodes that is created by
the following statements.
Node *p0 = new Node(000);
Node *p1 = p0->next = new Node(010);
Node *p2 = p1->next = new Node(020, p1);
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 37