Page 43 - DCAP605_ADVANCED_DATA_STRUCTURE_AND_ALGORITHMS
P. 43
Advanced Data Structure and Algorithms
Notes 2.7 Doubly Linked Lists
In the single linked list each node provides information about where the next node is in the list.
It faces difficulty if we are pointing to a specific node, then we can move only in the direction
of the links. It has no idea about where the previous node lies in memory. The only way to fi nd
the node which precedes that specific node is to start back at the beginning of the list. The same
problem arises when one wishes to delete an arbitrary node from a single linked list. Since in
order to easily delete an arbitrary node one must know the preceding node. This problem can
be avoided by using Doubly Linked List, we can store in each node not only the address of next
node but also the address of the previous node in the linked list. A node in Doubly Linked List
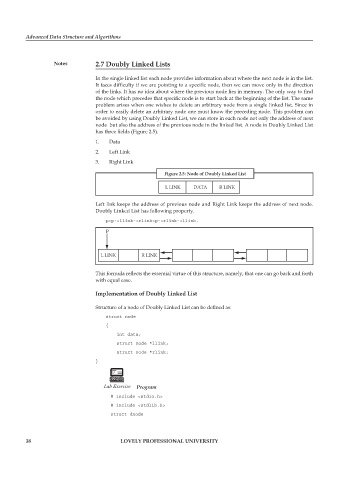
has three fields (Figure 2.5).
1. Data
2. Left Link
3. Right Link
Figure 2.5: Node of Doubly Linked List
L LINK DATA R LINK
Left link keeps the address of previous node and Right Link keeps the address of next node.
Doubly Linked List has following property.
p=p->llink->rlink=p->rlink->llink.
p
L LINK R LINK
This formula reflects the essential virtue of this structure, namely, that one can go back and forth
with equal ease.
Implementation of Doubly Linked List
Structure of a node of Doubly Linked List can be defi ned as:
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *llink;
struct node *rlink;
}
Lab Exercise Program
# include <stdio.h>
# include <stdlib.h>
struct dnode
38 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY