Page 254 - DCAP311_DCAP607_WIRELESS_NETWORKS
P. 254
Wireless Networks
Notes 14.5 The 802.1X
The 802.1X-2001 standard states:
"Port-based network access control makes use of the physical access characteristics of IEEE
802 LAN infrastructures in order to provide a means ofauthenticating and authorizing devices
attached to a LAN port that has point-to-point connection characteristics, and of preventing
access to that port in cases which the authentication and authorization fails. A port in this context
is a single point of attachment to the LAN infrastructure."
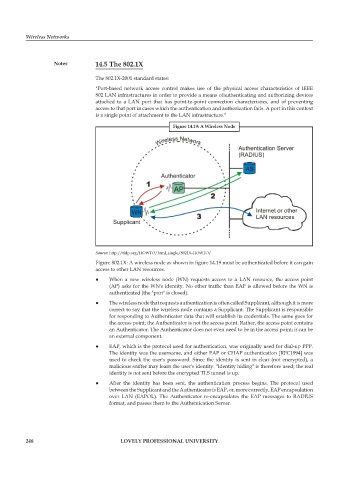
Figure 14.19: A Wireless Node
Source: http://tldp.org/HOWTO/html_single/8021X-HOWTO/
Figure 802.1X: A wireless node as shown in figure 14.19 must be authenticated before it can gain
access to other LAN resources.
z z When a new wireless node (WN) requests access to a LAN resource, the access point
(AP) asks for the WN's identity. No other traffic than EAP is allowed before the WN is
authenticated (the "port" is closed).
z z The wireless node that requests authentication is often called Supplicant, although it is more
correct to say that the wireless node contains a Supplicant. The Supplicant is responsible
for responding to Authenticator data that will establish its credentials. The same goes for
the access point; the Authenticator is not the access point. Rather, the access point contains
an Authenticator. The Authenticator does not even need to be in the access point; it can be
an external component.
z z EAP, which is the protocol used for authentication, was originally used for dial-up PPP.
The identity was the username, and either PAP or CHAP authentication [RFC1994] was
used to check the user's password. Since the identity is sent in clear (not encrypted), a
malicious sniffer may learn the user's identity. "Identity hiding" is therefore used; the real
identity is not sent before the encrypted TLS tunnel is up.
z z After the identity has been sent, the authentication process begins. The protocol used
between the Supplicant and the Authenticator is EAP, or, more correctly, EAP encapsulation
over LAN (EAPOL). The Authenticator re-encapsulates the EAP messages to RADIUS
format, and passes them to the Authentication Server.
248 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY