Page 255 - DCAP311_DCAP607_WIRELESS_NETWORKS
P. 255
Unit 14: Authentication
z z During authentication, the Authenticator just relays packets between the Supplicant and Notes
the Authentication Server. When the authentication process finishes, the Authentication
Server sends a success message (or failure, if the authentication failed). The Authenticator
then opens the "port" for the Supplicant.
z z After a successful authentication, the Supplicant is granted access to other LAN resources/
Internet.
Authentication means making sure that something is what it claims to be. E.g., in online banking,
you want to make sure that the remote computer is actually your bank, and not someone
pretending to be your bank. The purpose of 802.1x is to accept or reject users who want full
access to a network using 802.1x. It is a security protocol that works with 802.11 wireless
networks such as 802.11g and 802.11b, as well as with wired devices. The Authenticator deals
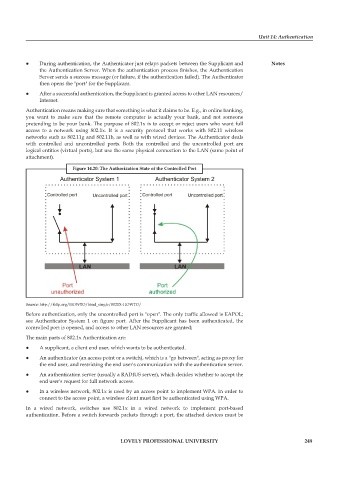
with controlled and uncontrolled ports. Both the controlled and the uncontrolled port are
logical entities (virtual ports), but use the same physical connection to the LAN (same point of
attachment).
Figure 14.20: The Authorization State of the Controlled Port
Source: http://tldp.org/HOWTO/html_single/8021X-HOWTO/
Before authentication, only the uncontrolled port is "open". The only traffic allowed is EAPOL;
see Authenticator System 1 on figure port. After the Supplicant has been authenticated, the
controlled port is opened, and access to other LAN resources are granted;
The main parts of 802.1x Authentication are:
z z A supplicant, a client end user, which wants to be authenticated.
z z An authenticator (an access point or a switch), which is a "go between", acting as proxy for
the end user, and restricting the end user's communication with the authentication server.
z z An authentication server (usually a RADIUS server), which decides whether to accept the
end user's request for full network access.
z z In a wireless network, 802.1x is used by an access point to implement WPA. In order to
connect to the access point, a wireless client must first be authenticated using WPA.
In a wired network, switches use 802.1x in a wired network to implement port-based
authentication. Before a switch forwards packets through a port, the attached devices must be
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 249