Page 83 - DCAP608_REAL TIME SYSTEMS
P. 83
Real Time Systems
Notes
To model the system in Prism, we discredit time and, to simplify the modelling process,
the division of one time unit is such that, for each of the possible frequencies, the number
of discrete time steps required by a task to finish on its WCET is an integer. For example,
if a task is run at the frequency 0.75 and the task takes WCET time units, it will require
WCET*4/3 time units to complete. Furthermore, we suppose that the completion time
distribution of a task is uniformly distributed between 1 and its WCET.
Results:
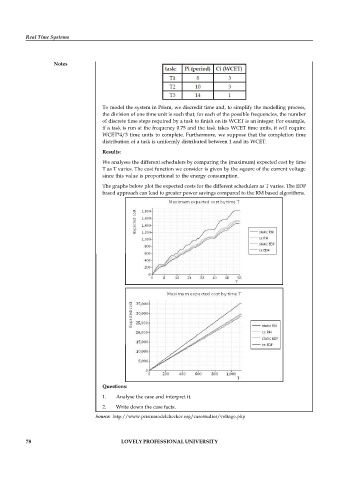
We analyses the different schedulers by comparing the (maximum) expected cost by time
T as T varies. The cost function we consider is given by the square of the current voltage
since this value is proportional to the energy consumption.
The graphs below plot the expected costs for the different schedulers as T varies. The EDF
based approach can lead to greater power savings compared to the RM based algorithms.
Questions:
1. Analyse the case and interpret it.
2. Write down the case facts.
Source: http://www.prismmodelchecker.org/casestudies/voltage.php
78 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY