Page 238 - DCAP403_Operating System
P. 238
Unit 12: Security Solution
The encryption algorithm specified in this standard is commonly known among those using Notes
the standard. The unique key chosen for use in a particular application makes the results of
encrypting data using the algorithm unique. Selection of a different key causes the cipher that
is produced for any given set of inputs to be different. The cryptographic security of the data
depends on the security provided for the key used to encipher and decipher the data.
Data can be recovered from cipher only by using exactly the same key used to encipher it.
Unauthorized recipients of the cipher whop know the algorithm but do not have the correct key
cannot drive the original data algorithmically. However, anyone who does have the key and
the algorithm can easily decipher the cipher and obtain the original data. A standard algorithm
based on a secure key thus provides a basis for exchanging encrypted computer data by issuing
the key used to encipher it to those unauthorized to have the data.
Data that is considered sensitive by the responsible authority, data that, has a high value, or
data that represents a high value should be cryptographically protected if it is vulnerable to
unauthorized disclosure or undetected modification during transmission or while in storage. A
risk analysis should be performed under the direction of a responsible authority to determine
potential threats. The costs of providing cryptographic protection using this standards as well as
alternative methods of providing this protection and their respective costs should be projected.
A responsible authority then should make a decision, based on these analyses, whether or not to
use cryptographic protection and this standard.
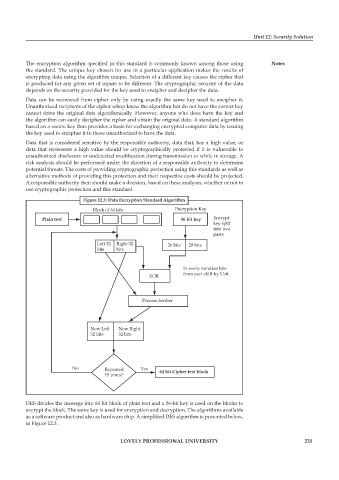
Figure 12.3: Data Encryption Standard Algorithm
Block of 64 bits Encryption Key
Plain text 56 bit key Encrypt
key split
into two
parts
Left 32 Right 32 26 bits 28 bits
bits bits
In every iteration bits
XOR from part shift by 1 bit
Process further
New Left New Right
32 bits 32 bits
No Repeated Yes 64 bit Cipher text block
15 times?
DES divides the message into 64 bit block of plain text and a 56-bit key is used on the blocks to
encrypt the block. The same key is used for encryption and decryption. The algorithms available
as a software product and also as hardware chip. A simplified DES algorithm is presented below,
in Figure 12.3.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 231