Page 11 - DCAP407_DATA_STRUCTURE
P. 11
Data Structure
Generally, there are three classes of integers namely, short int, int and long int. As shown in table 1.1,
short integers occupy only 1 byte, int occupies 2 bytes and the long integers occupy 4 bytes of memory.
Long integers can store longer range of values when compared to integer and short integer.
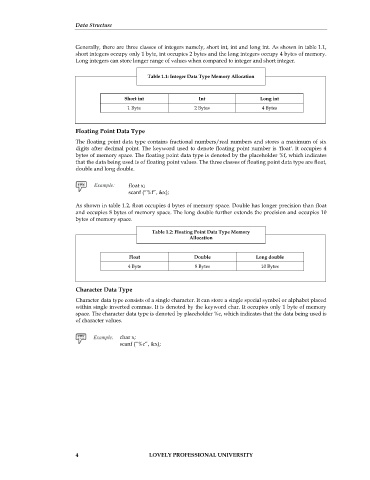
Table 1.1: Integer Data Type Memory Allocation
Short int Int Long int
1 Byte 2 Bytes 4 Bytes
Floating Point Data Type
The floating point data type contains fractional numbers/real numbers and stores a maximum of six
digits after decimal point. The keyword used to denote floating point number is 'float'. It occupies 4
bytes of memory space. The floating point data type is denoted by the placeholder %f, which indicates
that the data being used is of floating point values. The three classes of floating point data type are float,
double and long double.
float x;
scanf (“%f”, &x);
As shown in table 1.2, float occupies 4 bytes of memory space. Double has longer precision than float
and occupies 8 bytes of memory space. The long double further extends the precision and occupies 10
bytes of memory space.
Table 1.2: Floating Point Data Type Memory
Allocation
Float Double Long double
4 Byte 8 Bytes 10 Bytes
Character Data Type
Character data type consists of a single character. It can store a single special symbol or alphabet placed
within single inverted commas. It is denoted by the keyword char. It occupies only 1 byte of memory
space. The character data type is denoted by placeholder %c, which indicates that the data being used is
of character values.
char x;
scanf (“%c”, &x);
4 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY