Page 16 - DCAP407_DATA_STRUCTURE
P. 16
Unit 1: Introduction to Data Structures
Many different names are used for the data elements of a data structure. Some
examples are “data element”, “data object”, “node” and “record”. The specific name
that is used depends on the type of data structure.
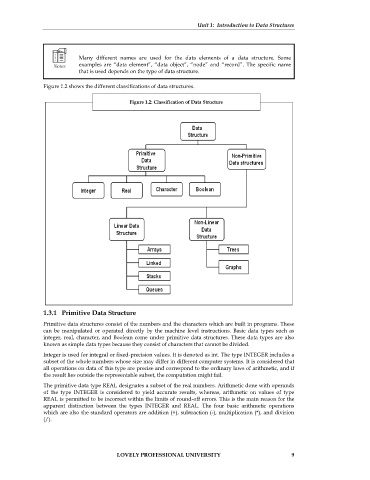
Figure 1.2 shows the different classifications of data structures.
Figure 1.2: Classification of Data Structure
1.3.1 Primitive Data Structure
Primitive data structures consist of the numbers and the characters which are built in programs. These
can be manipulated or operated directly by the machine level instructions. Basic data types such as
integer, real, character, and Boolean come under primitive data structures. These data types are also
known as simple data types because they consist of characters that cannot be divided.
Integer is used for integral or fixed-precision values. It is denoted as int. The type INTEGER includes a
subset of the whole numbers whose size may differ in different computer systems. It is considered that
all operations on data of this type are precise and correspond to the ordinary laws of arithmetic, and if
the result lies outside the representable subset, the computation might fail.
The primitive data type REAL designates a subset of the real numbers. Arithmetic done with operands
of the type INTEGER is considered to yield accurate results, whereas, arithmetic on values of type
REAL is permitted to be incorrect within the limits of round-off errors. This is the main reason for the
apparent distinction between the types INTEGER and REAL. The four basic arithmetic operations
which are also the standard operators are addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), and division
(/).
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 9