Page 152 - DCAP506_ARTIFICIAL_INTELLIGENCE
P. 152
Artificial Intelligence
Notes We develop first a pattern from some basic use cases. We then use analogy to apply it to a
different situation, then we generalize it and finally we produce another pattern for another
application specializing the abstract pattern. We then show how to use these patterns in building
conceptual models.
Example: Consider a design for a computer repair shop. The specifications for this
application are: A computer repair shop fixes broken computers. The shop is part of a chain of
similar shops. Customers bring computers to the shop for repair and a reception technician
makes an estimate. If the customer agrees, the computer is assigned for repair to some repair
technician, who keeps a Repair Event document. All the Repair Event documents for a computer
are collected in its repair log. A repair event may be suspended because of a lack of parts or other
reasons.
These requirements correspond to two basic Use Cases:
Get an estimate for a repair
Repair a computer
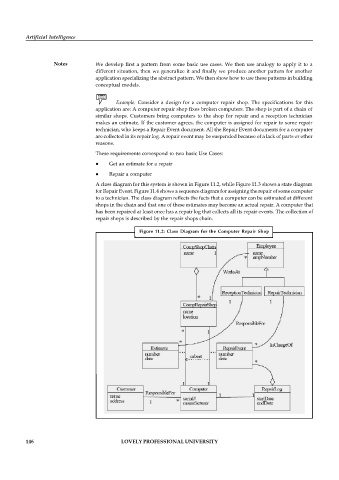
A class diagram for this system is shown in Figure 11.2, while Figure 11.3 shows a state diagram
for Repair Event. Figure 11.4 shows a sequence diagram for assigning the repair of some computer
to a technician. The class diagram reflects the facts that a computer can be estimated at different
shops in the chain and that one of these estimates may become an actual repair. A computer that
has been repaired at least once has a repair log that collects all its repair events. The collection of
repair shops is described by the repair shops chain.
Figure 11.2: Class Diagram for the Computer Repair Shop
146 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY