Page 71 - DCAP506_ARTIFICIAL_INTELLIGENCE
P. 71
Unit 5: Knowledge Representation
Notes
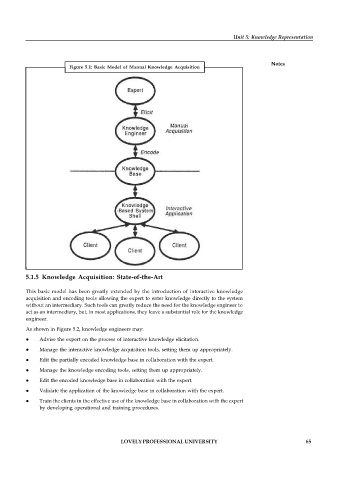
Figure 5.1: Basic Model of Manual Knowledge Acquisition
5.1.5 Knowledge Acquisition: State-of-the-Art
This basic model has been greatly extended by the introduction of interactive knowledge
acquisition and encoding tools allowing the expert to enter knowledge directly to the system
without an intermediary. Such tools can greatly reduce the need for the knowledge engineer to
act as an intermediary, but, in most applications, they leave a substantial role for the knowledge
engineer.
As shown in Figure 5.2, knowledge engineers may:
Advise the expert on the process of interactive knowledge elicitation.
Manage the interactive knowledge acquisition tools, setting them up appropriately.
Edit the partially encoded knowledge base in collaboration with the expert.
Manage the knowledge encoding tools, setting them up appropriately.
Edit the encoded knowledge base in collaboration with the expert.
Validate the application of the knowledge base in collaboration with the expert.
Train the clients in the effective use of the knowledge base in collaboration with the expert
by developing operational and training procedures.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 65