Page 178 - DCAP512_WAP_AND_WML
P. 178
WAP & WML
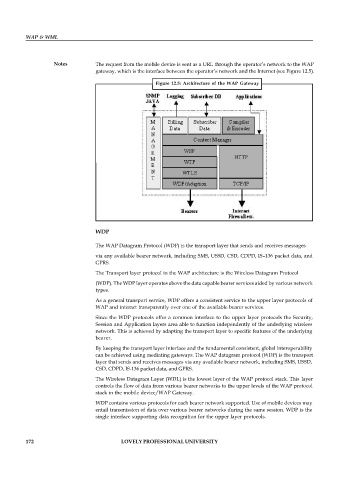
Notes The request from the mobile device is sent as a URL through the operator’s network to the WAP
gateway, which is the interface between the operator’s network and the Internet (see Figure 12.5).
Figure 12.5: Architecture of the WAP Gateway
WDP
The WAP Datagram Protocol (WDP) is the transport layer that sends and receives messages
via any available bearer network, including SMS, USSD, CSD, CDPD, IS–136 packet data, and
GPRS.
The Transport layer protocol in the WAP architecture is the Wireless Datagram Protocol
(WDP). The WDP layer operates above the data capable bearer services aided by various network
types.
As a general transport service, WDP offers a consistent service to the upper layer protocols of
WAP and interact transparently over one of the available bearer services.
Since the WDP protocols offer a common interface to the upper layer protocols the Security,
Session and Application layers area able to function independently of the underlying wireless
network. This is achieved by adapting the transport layer to specific features of the underlying
bearer.
By keeping the transport layer interface and the fundamental consistent, global interoperability
can be achieved using mediating gateways. The WAP datagram protocol (WDP) is the transport
layer that sends and receives messages via any available bearer network, including SMS, USSD,
CSD, CDPD, IS-136 packet data, and GPRS.
The Wireless Datagram Layer (WDL) is the lowest layer of the WAP protocol stack. This layer
controls the flow of data from various bearer networks to the upper levels of the WAP protocol
stack in the mobile device/WAP Gateway.
WDP contains various protocols for each bearer network supported. Use of mobile devices may
entail transmission of data over various bearer networks during the same session. WDP is the
single interface supporting data recognition for the upper layer protocols.
172 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY