Page 176 - DCAP512_WAP_AND_WML
P. 176
WAP & WML
Notes
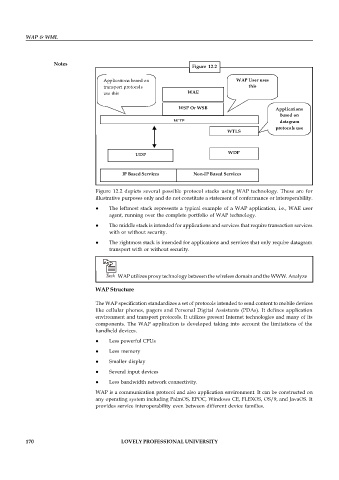
Figure 12.2
Applications based on WAP User uses
transport protocols this
use this WAE
WSP Or WSB Applications
based on
WTP datagram
protocols use
WTLS
this
WDP
UDP
IP Based Services Non-IP Based Services
Figure 12.2 depicts several possible protocol stacks using WAP technology. These are for
illustrative purposes only and do not constitute a statement of conformance or interoperability.
The leftmost stack represents a typical example of a WAP application, i.e., WAE user
agent, running over the complete portfolio of WAP technology.
The middle stack is intended for applications and services that require transaction services
with or without security.
The rightmost stack is intended for applications and services that only require datagram
transport with or without security.
Task WAP utilizes proxy technology between the wireless domain and the WWW. Analyze
WAP Structure
The WAP specification standardizes a set of protocols intended to send content to mobile devices
like cellular phones, pagers and Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs). It defines application
environment and transport protocols. It utilizes present Internet technologies and many of its
components. The WAP application is developed taking into account the limitations of the
handheld devices.
Less powerful CPUs
Less memory
Smaller display
Several input devices
Less bandwidth network connectivity.
WAP is a communication protocol and also application environment. It can be constructed on
any operating system including PalmOS, EPOC, Windows CE, FLEXOS, OS/9, and JavaOS. It
provides service interoperability even between different device families.
170 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY