Page 158 - DCAP606_BUSINESS_INTELLIGENCE
P. 158
Unit 11: Data Mining
2. ......................... are any facts, numbers, or text that can be processed by a computer. Notes
3. The patterns, associations, or relationships among all types of data can provide
...................................
11.2 Data Mining Approaches
Two widespread data mining methods for finding concealed patterns in data are clustering and
classification analysis. Although classification and clustering are often cited in the identical
breath, they are different analytical advances.
Imaging a database of customer records, where each record represents a customer’s attributes.
These can encompass identifiers such as name and address, demographic data such as gender
and age, and financial attributes such as income and revenue spent.
Clustering is an automated method to group associated records together. Related records are
grouped together on the basis of similar values for attributes.
Notes This approach of segmenting the database via clustering analysis is often used as an
exploratory technique because it is not necessary for the end-user/analyst to identify
ahead of time how records should be associated simultaneously.
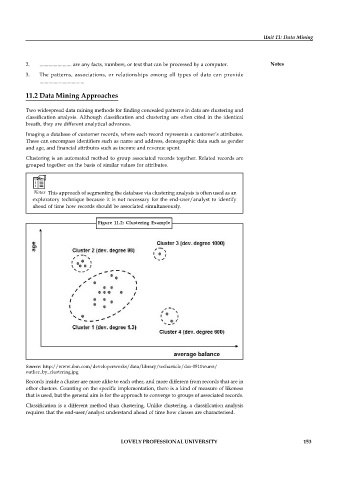
Figure 11.2: Clustering Example
Source: http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/data/library/techarticle/dm-0811wurst/
outlier_by_clustering.jpg
Records inside a cluster are more alike to each other, and more different from records that are in
other clusters. Counting on the specific implementation, there is a kind of measure of likeness
that is used, but the general aim is for the approach to converge to groups of associated records.
Classification is a different method than clustering. Unlike clustering, a classification analysis
requires that the end-user/analyst understand ahead of time how classes are characterised.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 153