Page 57 - DMGT104_FINANCIAL_ACCOUNTING
P. 57
Unit 4: Accounting Equation and Accounting Cycle
company provides a service and allows the client to pay in 30 days, the company has increased Notes
its assets (Accounts Receivable) and has also increased its owner’s equity because it has earned
service revenue. If the company runs a radio advertisement and agrees to pay later, the company
will incur an expense that will reduce owner’s equity and has increased its liabilities.
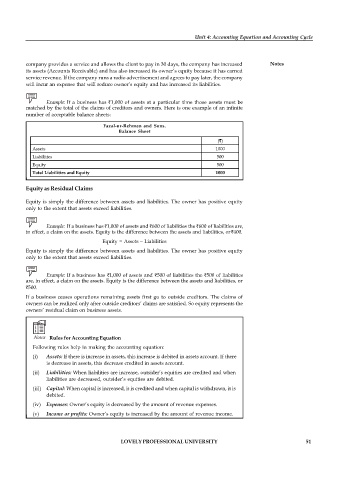
Example: If a business has 1,000 of assets at a particular time those assets must be
matched by the total of the claims of creditors and owners. Here is one example of an infinite
number of acceptable balance sheets:
Fazal-ur-Rehman and Sons.
Balance Sheet
( )
Assets 1000
Liabilities 500
Equity 500
Total Liabilities and Equity 1000
Equity as Residual Claims
Equity is simply the difference between assets and liabilities. The owner has positive equity
only to the extent that assets exceed liabilities.
Example: If a business has 1,000 of assets and 600 of liabilities the 600 of liabilities are,
in effect, a claim on the assets. Equity is the difference between the assets and liabilities, or 400.
Equity = Assets – Liabilities
Equity is simply the difference between assets and liabilities. The owner has positive equity
only to the extent that assets exceed liabilities.
Example: If a business has 1,000 of assets and 500 of liabilities the 500 of liabilities
are, in effect, a claim on the assets. Equity is the difference between the assets and liabilities, or
500.
If a business ceases operations remaining assets first go to outside creditors. The claims of
owners can be realized only after outside creditors’ claims are satisfied. So equity represents the
owners’ residual claim on business assets.
Notes Rules for Accounting Equation
Following rules help in making the accounting equation:
(i) Assets: If there is increase in assets, this increase is debited in assets account. If there
is decrease in assets, this decrease credited in assets account.
(ii) Liabilities: When liabilities are increase, outsider’s equities are credited and when
liabilities are decreased, outsider’s equities are debited.
(iii) Capital: When capital is increased, it is credited and when capital is withdrawn, it is
debited.
(iv) Expenses: Owner’s equity is decreased by the amount of revenue expenses.
(v) Income or profits: Owner’s equity is increased by the amount of revenue income.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 51