Page 63 - DMGT104_FINANCIAL_ACCOUNTING
P. 63
Unit 4: Accounting Equation and Accounting Cycle
(d) Revenue Accounts: Revenue accounts include the transactions relating to income, Notes
commission, interest, dividend, sales, etc.
(e) Expenses Accounts: These include those accounts which are relating to the expenses
of business as repairs, rent, maintenance, insurance and lighting, etc.
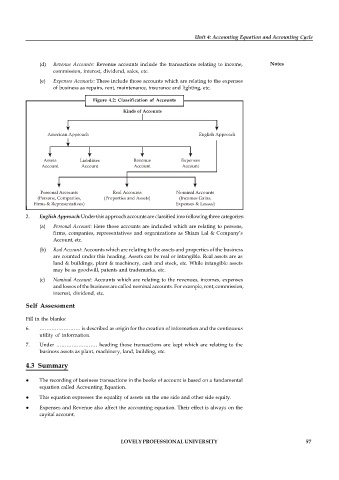
Figure 4.2: Classification of Accounts
Kinds of Accounts
American Approach English Approach
Assets Liabilities Revenue Expenses
Account Account Account Account
Personal Accounts Real Accounts Nominal Accounts
(Persons, Companies, (Properties and Assets) (Incomes Gains,
Firms & Representatives) Expenses & Losses)
2. English Approach: Under this approach accounts are classified into following three categories:
(a) Personal Account: Here those accounts are included which are relating to persons,
firms, companies, representatives and organizations as Shiam Lal & Company’s
Account, etc.
(b) Real Account: Accounts which are relating to the assets and properties of the business
are counted under this heading. Assets can be real or intangible. Real assets are as
land & buildings, plant & machinery, cash and stock, etc. While intangible assets
may be as goodwill, patents and trademarks, etc.
(c) Nominal Account: Accounts which are relating to the revenues, incomes, expenses
and losses of the business are called nominal accounts. For example, rent, commission,
interest, dividend, etc.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
6. …………………… is described as origin for the creation of information and the continuous
utility of information.
7. Under …………………… heading those transactions are kept which are relating to the
business assets as plant, machinery, land, building, etc.
4.3 Summary
The recording of business transactions in the books of account is based on a fundamental
equation called Accounting Equation.
This equation expresses the equality of assets on the one side and other side equity.
Expenses and Revenue also affect the accounting equation. Their effect is always on the
capital account.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 57