Page 178 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 178
Unit 8: Correlation Analysis
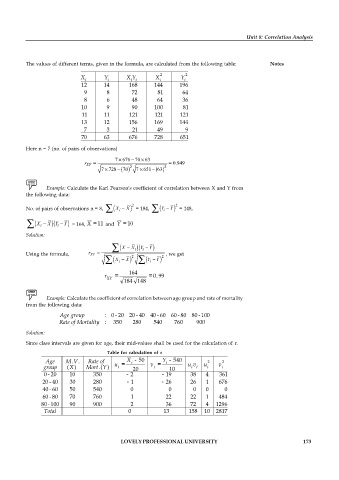
The values of different terms, given in the formula, are calculated from the following table: Notes
2 2
X Y X Y X Y
i i i i i i
12 14 168 144 196
9 8 72 81 64
8 6 48 64 36
10 9 90 100 81
11 11 121 121 121
13 12 156 169 144
7 3 21 49 9
70 63 676 728 651
Here n = 7 (no. of pairs of observations)
7 676 70 63
r XY 0.949
7 728 70 2 7 651 63 2
Example: Calculate the Karl Pearson's coefficient of correlation between X and Y from
the following data:
2 2
No. of pairs of observations n = 8, X i X = 184, Y i Y = 148,
X i X Y i Y = 164, X =11 and Y =10
Solution:
X X i Y i Y
Using the formula, r XY , we get
2 2
X i X Y i Y
164
r = =0.99
XY
184 148
Example: Calculate the coefficient of correlation between age group and rate of mortality
from the following data:
Age group : 0 - 20 20 - 40 40 - 60 60 - 80 80 -100
Rate of Mortality : 350 280 540 760 900
Solution:
Since class intervals are given for age, their mid-values shall be used for the calculation of r.
Table for calculation of r
Age M.V. Rate of u = X - 50 v = Y - 540 2 2
i
i
group (X) Mort.(Y) i 20 i 10 u v u i v i
i i
0 - 20 10 350 - 2 - 19 38 4 361
20 - 40 30 280 - 1 - 26 26 1 676
40 - 60 50 540 0 0 0 0 0
60 - 80 70 760 1 22 22 1 484
80 -100 90 900 2 36 72 4 1296
Total 0 13 158 10 2817
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 173