Page 179 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 179
Quantitative Techniques – I
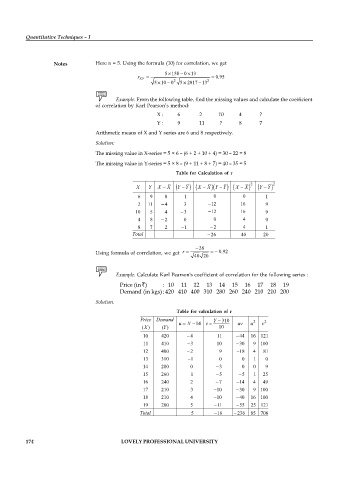
Notes Here n = 5. Using the formula (10) for correlation, we get
5 158 0 13
r XY 0.95
5 10 0 2 5 2817 13 2
Example: From the following table, find the missing values and calculate the coefficient
of correlation by Karl Pearson’s method:
X : 6 2 10 4 ?
Y : 9 11 ? 8 7
Arithmetic means of X and Y series are 6 and 8 respectively.
Solution:
The missing value in X-series = 5 × 6 – (6 + 2 + 10 + 4) = 30 – 22 = 8
The missing value in Y-series = 5 × 8 – (9 + 11 + 8 + 7) = 40 – 35 = 5
Table for Calculation of r
2 2
X Y X X Y Y X X Y Y X X Y Y
6 9 0 1 0 0 1
2 11 4 3 12 16 9
10 5 4 3 12 16 9
4 8 2 0 0 4 0
8 7 2 1 2 4 1
Total 26 40 20
26
Using formula of correlation, we get r 0.92
40 20
Example: Calculate Karl Pearson's coefficient of correlation for the following series :
Price (in ) : 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
Demand (in kgs) : 420 410 400 310 280 260 240 210 210 200
Solution.
Table for calculation of r
Price Demand Y 310 2 2
u X 14 v uv u v
X
Y
( ) ( ) 10
10 420 4 11 44 16 121
11 410 3 10 30 9 100
12 400 2 9 18 4 81
13 310 1 0 0 1 0
14 280 0 3 0 0 9
15 260 1 5 5 1 25
16 240 2 7 14 4 49
17 210 3 10 30 9 100
18 210 4 10 40 16 100
19 200 5 11 55 25 121
Total 5 16 236 85 706
174 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY