Page 10 - DMGT202_COST_AND_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 10
Unit 1: Introduction to Cost Accounting
6. Financial accounts display results in total profits whereas cost accounts give the results of Notes
each operation.
7. All expenses such as interest on capital, depreciation, etc., are normally charged in
financial accounts, which reveals the true and fair affairs of business in general and cost of
production in particular. In case of cost accounting, where certain expenses are eliminated
or deleted the cost per unit will be generally unfair.
8. Financial accounting will generally present a better picture to the public who can
not understand the intricacies of the maintenance of accounting. Cost accounting, in
particular, is always beneficial from the point of management, rather than from the public
undertaking.
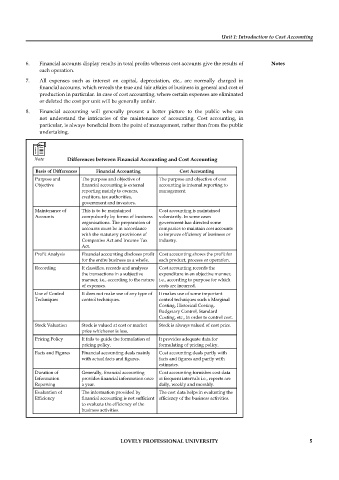
Note Differences between Financial Accounting and Cost Accounting
Basis of Differences Financial Accounting Cost Accounting
Purpose and The purpose and objective of The purpose and objective of cost
Objective financial accounting is external accounting is internal reporting to
reporting mainly to owners, management.
creditors, tax authorities,
government and investors.
Maintenance of This is to be maintained Cost accounting is maintained
Accounts compulsorily by forms of business voluntarily. In some cases
organisations. The preparation of government has directed some
accounts must be in accordance companies to maintain cost accounts
with the statutory provisions of to improve efficiency of business or
Companies Act and Income Tax industry.
Act.
Profi t Analysis Financial accounting discloses profi t Cost accounting shows the profi t for
for the entire business as a whole. each product, process or operation.
Recording It classifies, records and analyses Cost accounting records the
the transactions in a subjective expenditure in an objective manner,
manner, i.e., according to the nature i.e., according to purpose for which
of expenses. costs are incurred.
Use of Control It does not make use of any type of It makes use of some important
Techniques control techniques. control techniques such a Marginal
Costing, Historical Costing,
Budgetary Control, Standard
Costing, etc., in order to control cost.
Stock Valuation Stock is valued at cost or market Stock is always valued of cost price.
price whichever is less.
Pricing Policy It fails to guide the formulation of It provides adequate data for
pricing policy. formulating of pricing policy.
Facts and Figures Financial accounting deals mainly Cost accounting deals partly with
with actual facts and fi gures. facts and figures and partly with
estimates.
Duration of Generally, fi nancial accounting Cost accounting furnishes cost data
Information provides financial information once at frequent intervals i.e., reports are
Reporting a year. daily, weekly and monthly.
Evaluation of The information provided by The cost data helps in evaluating the
Effi ciency financial accounting is not suffi cient effi ciency of the business activities.
to evaluate the efficiency of the
business activities.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 5