Page 14 - DMGT202_COST_AND_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 14
Unit 1: Introduction to Cost Accounting
1.6 Elements of Cost Notes
The correct of interpretation of the term ‘cost’ may also be understood by having knowledge
about basic elements of cost. These elements have been shown in the following fi gure.
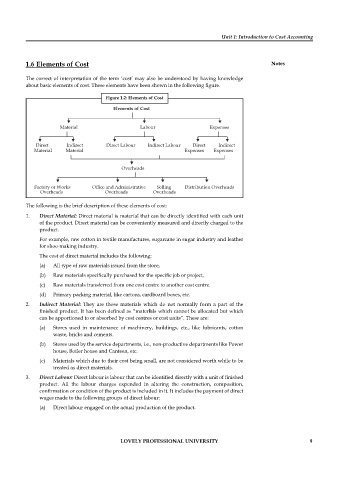
Figure 1.2: Elements of Cost
Elements of Cost
Material Labour Expenses
Direct Indirect Direct Labour Indirect Labour Direct Indirect
Material Material Expenses Expenses
Overheads
Factory or Works Office and Administrative Selling Distribution Overheads
Overheads Overheads Overheads
The following is the brief description of these elements of cost:
1. Direct Material: Direct material is material that can be directly identified with each unit
of the product. Direct material can be conveniently measured and directly charged to the
product.
For example, raw cotton in textile manufactures, sugarcane in sugar industry and leather
for shoe-making industry.
The cost of direct material includes the following:
(a) All type of raw materials issued from the store,
(b) Raw materials specifically purchased for the specific job or project,
(c) Raw materials transferred from one cost centre to another cost centre.
(d) Primary packing material, like cartons, cardboard boxes, etc.
2. Indirect Material: They are those materials which do not normally form a part of the
finished product. It has been defined as “materials which cannot be allocated but which
can be apportioned to or absorbed by cost centres or cost units”. These are:
(a) Stores used in maintenance of machinery, buildings, etc., like lubricants, cotton
waste, bricks and cements.
(b) Stores used by the service departments, i.e., non-productive departments like Power
house, Boiler house and Canteen, etc.
(c) Materials which due to their cost being small, are not considered worth while to be
treated as direct materials.
3. Direct Labour: Direct labour is labour that can be identified directly with a unit of fi nished
product. All the labour charges expended in altering the construction, composition,
confirmation or condition of the product is included in it. It includes the payment of direct
wages made to the following groups of direct labour:
(a) Direct labour engaged on the actual production of the product.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 9